Wireless Network Topologies Market By Topology Type (Point-to-Point (P2P), Point-to-Multipoint (P2MP), Mesh Network, Star Topology, Tree Topology, Hybrid Topologies), By Technology Type (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, Cellular), By End-Use Industry (Telecommunications, Information Technology, Healthcare, Transportation), By Application (Consumer Electronics, Industrial Automation, Internet of Things (IoT), Remote Monitoring and Sensing, Communication and Networking), By Deployment Mode (Cloud-based, On-premises), By Enterprise Size (Small, Medium Enterprises (SMEs) and Large Enterprises); Global Insights & Forecast (2024- 2030)
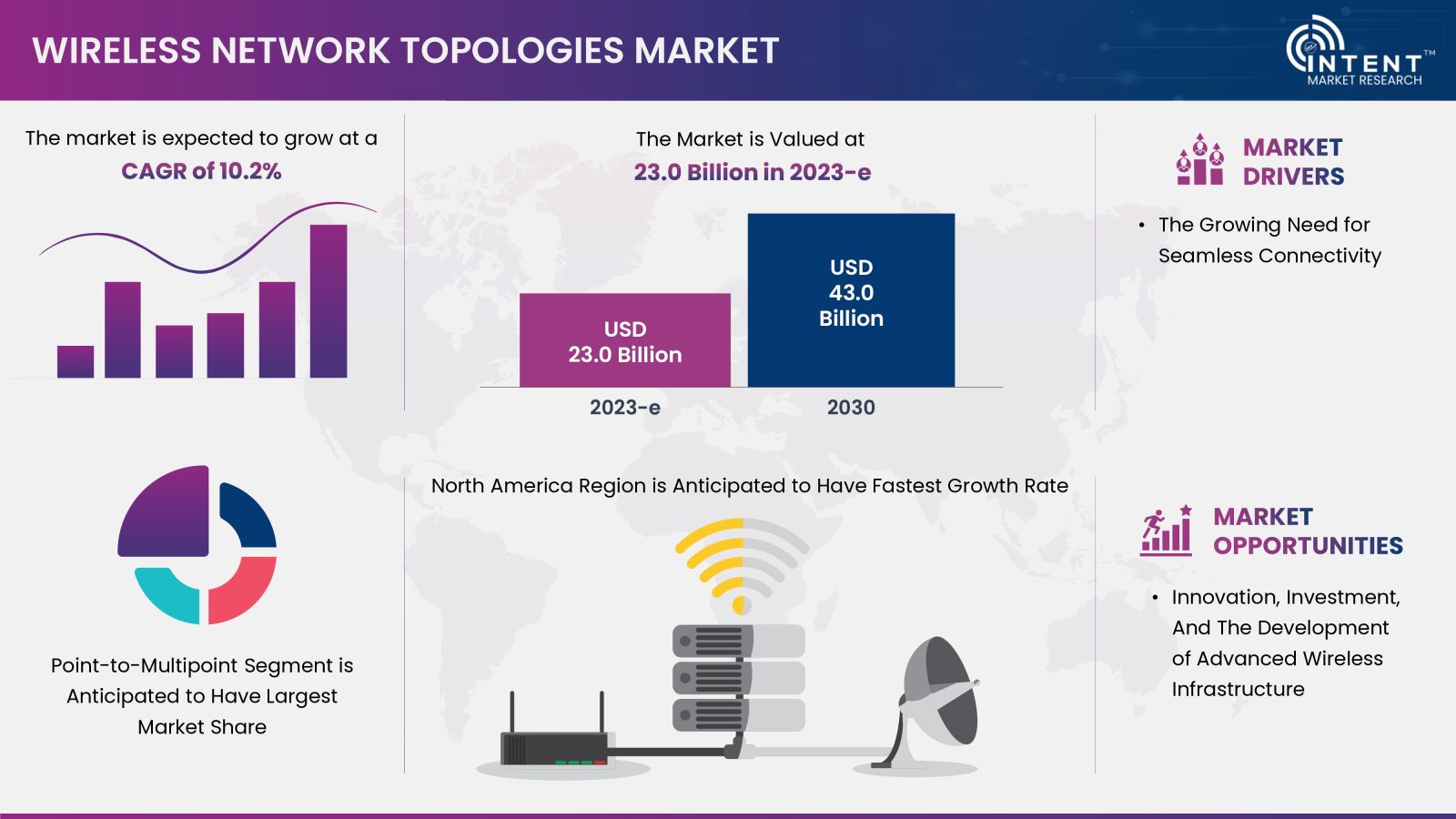
According to Intent Market Research, the Wireless Network Topologies Market is expected to grow from USD 23.0 billion in 2023-e at a CAGR of 10.2% to touch USD 43.0 billion by 2030. Prominent players include Aruba Networks, Cisco Systems, D-Link Corporation, Ericsson, Huawei Technologies, NETGEAR, Nokia Networks, Qualcomm, Ruckus Networks, Samsung Networks, TP-Link Technologies, Ubiquiti Networks & ZTE. Wireless network topologies lead to faster transfer of information within businesses between partners and customers i.e. driving the market growth.
Click here to: Get FREE Sample Pages of this Report
The term "wireless network topologies market" refers to the industry associated with the deployment, adoption, and utilization of various wireless network topologies in telecommunications, information technology, and connectivity sectors.
Wireless Network Topologies Market Dynamics
Innovation, Investment, and the Development of Advanced Wireless Infrastructure are Fostering Market Growth
The growing need for seamless connectivity across various devices, IoT (Internet of Things) devices, and emerging technologies such as smart homes, smart cities, and Industry 4.0 drives the demand for diverse wireless network topologies. These drivers collectively contribute to the growth of the wireless network topologies market, fostering innovation, investment, and the development of advanced wireless infrastructure to meet the demands of an increasingly connected world.
Increasing Risks of Cyber Threats, including Data Breaches, and Malware Attacks are Hindering the Market Growth
With the increased connectivity and data transmission, wireless networks become susceptible to cyber threats, including unauthorized access, data breaches, and malware attacks. As the number of connected devices increases, wireless network scalability becomes crucial. Achieving low latency and high reliability in wireless communication networks, especially for applications such as autonomous vehicles, remote surgeries, and real-time IoT, remains a significant challenge. These challenges need to be addressed to increase the adoption of technology among application industries.
Wireless Network Topologies Segment Insights
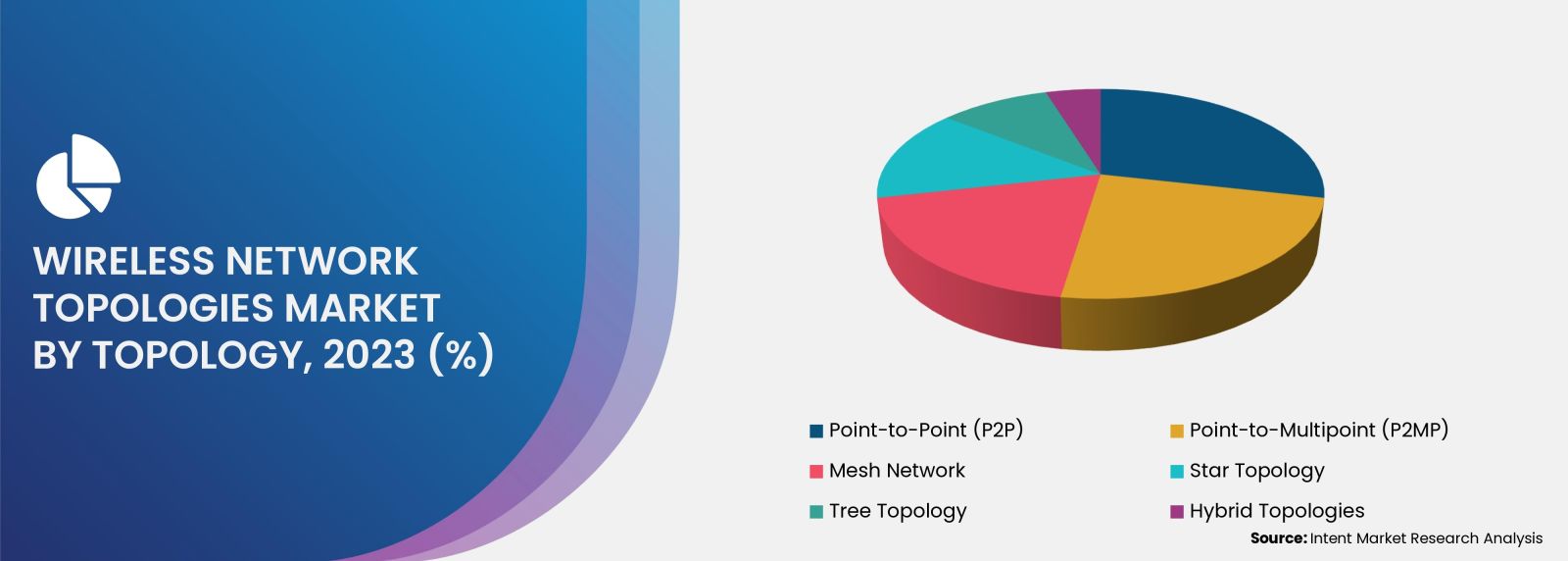
Rising Need for Centralized Management & Multiple Endpoints will Drive the P2MP Topology
Point-to-Multipoint (P2MP) wireless network topology involves establishing a single central point (hub or base station) that communicates with multiple endpoints or client devices. P2MP connections are commonly used in various wireless network deployments due to their ability to efficiently serve multiple clients from a single centralized location. Overall, P2MP topology is widely used in wireless network deployments, for efficient communication between a central hub and multiple endpoints spread across a coverage area.
The Demand for Wi-Fi is Increasing Continuously as It Offers Mobility and Flexibility
Wi-Fi technology enables wireless local area networking (WLAN) using radio waves to provide wireless connectivity to devices within a certain range of an access point (AP) or router. Wi-Fi networks often use a star topology, where multiple devices such as laptops, smartphones, tablets, and smart home devices connect wirelessly to a central access point (AP) or routerMesh networks interconnect multiple access points wirelessly, allowing devices to communicate with the nearest access point and potentially creating multiple paths for data transmission, enhancing coverage and reliability.
Wireless Network Topologies Enable the Seamless Functioning of Cellular Communications
Wireless network topologies serve as the fundamental infrastructure for telecommunications and mobile networks, enabling the seamless functioning of cellular communications, data transmission, and the delivery of mobile services to users. Wireless network topologies are fundamental to cellular networks, organizing communication into cells served by base stations. These networks employ various topologies, including a combination of point-to-multipoint and mesh configurations, to establish connections between mobile devices and base stations.
Rising Demand for Wireless Network Topologies in Communication & Networking is Fueling the Market Growth
Wireless network topologies enable cellular networks for voice calls, text messaging, mobile internet access, and other mobile services. Wireless networks support VoIP applications, facilitating voice calls and conferencing over the Internet as an alternative to traditional telephone networks. These networks also enable video conferencing, streaming services, and multimedia content delivery, empowering users to conduct virtual meetings, stream video content, and access entertainment platforms.
Wireless Network Topologies Enable Users to Leverage the Benefits of Cloud Computing, Storage, and Applications
Wireless networks provide the connectivity needed for users to access cloud-based services such as cloud storage, Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) applications, Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) offerings. Wireless networks enable remote workers to connect to cloud-based collaboration tools such as document sharing, video conferencing, project management platforms, and other collaborative applications, enhancing productivity and communication.
Large Enterprises Heavily Rely on Wireless Network Topologies to Create High-Performance and Secure Networks
The mobile networks in large enterprises require high-speed and reliable wireless connections to support critical business applications, data-intensive tasks, and real-time communications. As a result, large enterprises extensively utilize wireless network topologies to facilitate their complex operations & provide connectivity. Wireless networks enable enterprise mobility, allowing employees to access resources, applications, and data from various devices, regardless of their location within the enterprise premises or when working remotely.
Regional Insights
North America Market has Witnessed Significant Adoption of Wireless Technologies
North American companies and research institutions have been at the forefront of wireless technology innovation, contributing to the advancement of networking standards and infrastructure. The region has historically seen substantial adoption of wireless technologies, including mobile networks, Wi-Fi, and emerging technologies such as 5G, driven by consumer demand for connectivity and data services.
Competitive Landscape
Novel Product Launches are the Major Strategy Adopted by the Key Market Players
The wireless network topology market is moderately fragmented and needs large initial investment and infrastructure by enterprises. Prominent players include Aruba Networks, Cisco Systems, D-Link Corporation, Ericsson, Huawei Technologies, NETGEAR, Nokia Networks, Qualcomm, Ruckus Networks, Samsung Networks, TP-Link Technologies, Ubiquiti Networks & ZTE.
In June 2022, Huawei unveiled the HUAWEI Wi-Fi Mesh 7, extends its mesh router product line. The new Huawei smart mesh routers come in two packs and enable blazing-fast Wi-Fi 6 Plus connection rates for up to 250 devices within 6,000 square feet.
Click here to: Get your custom research report today
Wireless Network Topologies Market Coverage
The report provides key insights into the wireless network topologies market, and it focuses on technological developments, trends, and initiatives taken by the government. This sector analysis delves into market drivers, restraints, opportunities, and other pertinent factors, examining key players and the competitive landscape in the wireless network topologies market.
Report Scope
|
Report Features |
Description |
|
Market Size (2023-e) |
USD 23.0 billion |
|
Forecast Revenue (2030) |
USD 43.0 billion |
|
CAGR (2024-2030) |
10.2% |
|
Base Year for Estimation |
2023-e |
|
Historic Year |
2022 |
|
Forecast Period |
2024-2030 |
|
Report Coverage |
Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments |
|
Segments Covered |
By Topology Type (Point-to-Point (P2P), Point-to-Multipoint (P2MP), Mesh Network, Star Topology, Tree Topology & Hybrid Topologies), By Technology Type (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, Cellular, Others), By End-Use Industry (Telecommunications, Information Technology, Healthcare, Transportation, Others), By Application (Consumer Electronics, Industrial Automation, Internet of Things (IoT), Remote Monitoring & Sensing, Communication, Networking, Others), By Deployment Mode (Cloud-based & On-premises), By Enterprise Size (Small & Medium Enterprises (SMEs), Large Enterprises) |
|
Regional Analysis |
North America (US, Canada), Europe (Germany, France, UK, Italy,), Asia-Pacific (China, Japan, South Korea, India), Latin America (Brazil, Mexico, Argentina), Middle East and Africa (Saudi Arabia, South Africa, United Arab Emirates) |
|
Competitive Landscape |
Aruba Networks, Cisco Systems, D-Link Corporation, Ericsson, Huawei Technologies, NETGEAR, Nokia Networks, Qualcomm Technologies, Ruckus Networks, Samsung Networks, TP-Link Technologies, Ubiquiti Networks, ZTE Corporation |
|
Customization Scope |
Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. |
|
Purchase Options |
We have three licenses to opt for Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) |
|
1. Introduction |
|
1. 1. Study Assumptions and Wireless Network Topologies Market Definition |
|
1.2. Scope of the Study |
|
2. Research Methodology |
|
3. Executive Summary |
|
4. Wireless Network Topologies Market Dynamics |
|
4.1. Market Growth Drivers |
|
4.2 Market Growth Challenges |
|
5. Wireless Network Topologies Market Outlook |
|
5.1. Industry Entry Barriers |
|
5.2 Consumer Preference Analysis |
|
5.3. Case Study |
|
5.4 Key Raw Materials Suppliers and Price Analysis |
|
5.5. Regulatory Landscape |
|
5.6 Technological advances and future opportunity analysis |
|
5.7. Manufacturing Cost Structure Analysis |
|
5.8 Upstream and Downstream Analysis |
|
5.9. Pestle Analysis |
|
6. Global Wireless Network Topologies Market Segmentation (Market Size & Forecast: USD billion, 2024 – 2030) |
|
6.1 Topology Type |
|
6.1.1 Point-to-Point (P2P) |
|
6.1.2 Point-to-Multipoint (P2MP) |
|
6.1.3 Mesh Network |
|
6.1.4 Star Topology |
|
6.1.5 Tree Topology |
|
6.1.6 Hybrid Topologies |
|
6.2 Technology |
|
6.2.1 Wi-Fi |
|
6.2.2 Bluetooth |
|
6.2.3 Zigbee |
|
6.2.4 Cellular |
|
6.2.5 Others |
|
6.3 End-Use Industry |
|
6.3.1 Telecommunications |
|
6.3.2 Information Technology |
|
6.3.3 Healthcare |
|
6.3.4 Transportation |
|
6.3.5 Others |
|
6.4 Enterprise size |
|
6.4.1 Large Enterprises |
|
6.4.2 Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) |
|
6.5 Deployment Mode |
|
6.5.1 Cloud-based |
|
6.5.2 On-premises |
|
6.6 Application |
|
6.6.1 Consumer Electronics |
|
6.6.2 Industrial Automation |
|
6.6.3 Internet of Things (IoT) |
|
6.6.4 Remote Monitoring and Sensing |
|
6.6.5 Communication and Networking |
|
6.6.6 Others |
|
6.7 Geography |
|
6.7.1 North America |
|
6.7.2 Europe |
|
6.7.3 Asia-Pacific |
|
6.7.4 Latin America |
|
6.7.5 Middle East and Africa |
|
7. North America Wireless Network Topologies Market Segmentation (Market Size & Forecast: USD billion, 2024 – 2030) |
|
7.1 Topology Type |
|
7.1.1 Point-to-Point (P2P) |
|
7.1.2 Point-to-Multipoint (P2MP) |
|
7.1.3 Mesh Network |
|
7.1.4 Star Topology |
|
7.1.5 Tree Topology |
|
7.1.6 Hybrid Topologies |
|
7.2 Technology |
|
7.2.1 Wi-Fi |
|
7.2.2 Bluetooth |
|
7.2.3 Zigbee |
|
7.2.4 Cellular |
|
7.2.5 Others |
|
7.3 End-Use Industry |
|
7.3.1 Telecommunications |
|
7.3.2 Information Technology |
|
7.3.3 Healthcare |
|
7.3.4 Transportation |
|
7.3.5 Others |
|
7.4 Enterprise size |
|
7.4.1 Large Enterprises |
|
7.4.2 Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) |
|
7.5 Deployment Mode |
|
7.5.1 Cloud-based |
|
7.5.2 On-premises |
|
7.6 Application |
|
7.6.1 Consumer Electronics |
|
7.6.2 Industrial Automation |
|
7.6.3 Internet of Things (IoT) |
|
7.6.4 Remote Monitoring and Sensing |
|
7.6.5 Communication and Networking |
|
7.6.6 Others |
|
7.7 Country |
|
7.7.1 United States |
|
7.7.1.1 Topology Type |
|
7.7.1.1.1 Point-to-Point (P2P) |
|
7.7.1.1.2 Point-to-Multipoint (P2MP) |
|
7.7.1.1.3 Mesh Network |
|
7.7.1.1.4 Star Topology |
|
7.7.1.1.5 Tree Topology |
|
7.7.1.1.6 Hybrid Topologies |
|
7.7.1.2 Technology |
|
7.7.1.2.1 Wifi |
|
7.7.1.2.2 Bluetooth |
|
7.7.1.2.3 Zigbee |
|
7.7.1.2.4 Cellular |
|
7.7.1.2.5 Others |
|
7.7.1.3 End-Use Industry |
|
7.7.1.3.1 Telecommunications |
|
7.7.1.3.2 Information Technology |
|
7.7.1.3.3 Healthcare |
|
7.7.1.3.4 Transportation |
|
7.7.1.3.4 Others |
|
7.7.1.4 Enterprise size |
|
7.7.1.4.1 Large Enterprises |
|
7.7.1.4.2 Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) |
|
7.7.1.5 Deployment Mode |
|
7.7.1.5.1 Cloud-based |
|
7.7.1.5.2 On-premises |
|
7.7.1.6 Application |
|
7.7.1.6.1 Consumer Electronics |
|
7.7.1.6.2 Industrial Automation |
|
7.7.1.6.3 Internet of Things (IoT) |
|
7.7.1.6.4 Remote Monitoring and Sensing |
|
7.7.1.6.5 Communication and Networking |
|
7.7.1.6.6 Others |
|
7.7.2 Canada |
|
7.7.2.1 Topology Type |
|
7.7.2.1.1 Point-to-Point (P2P) |
|
7.7.2.1.2 Point-to-Multipoint (P2MP) |
|
7.7.2.1.3 Mesh Network |
|
7.7.2.1.4 Star Topology |
|
7.7.2.1.5 Tree Topology |
|
7.7.2.1.6 Hybrid Topologies |
|
7.7.2.2 Technology |
|
7.7.2.2.1 Wifi |
|
7.7.2.2.2 Bluetooth |
|
7.7.2.2.3 Zigbee |
|
7.7.2.2.4 Cellular |
|
7.7.2.2.5 Others |
|
7.7.2.3 End-Use Industry |
|
7.7.2.3.1 Telecommunications |
|
7.7.2.3.2 Information Technology |
|
7.7.2.3.3 Healthcare |
|
7.7.2.3.4 Transportation |
|
7.7.2.3.4 Others |
|
7.7.2.4 Enterprise size |
|
7.7.2.4.1 Large Enterprises |
|
7.7.2.4.2 Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) |
|
7.7.2.5 Deployment Mode |
|
7.7.2.5.1 Cloud-based |
|
7.7.2.5.2 On-premises |
|
7.7.2.6 Application |
|
7.7.2.6.1 Consumer Electronics |
|
7.7.2.6.2 Industrial Automation |
|
7.7.2.6.3 Internet of Things (IoT) |
|
7.7.2.6.4 Remote Monitoring and Sensing |
|
7.7.2.6.5 Communication and Networking |
|
7.7.2.6.6 Others |
|
8. Europe Market Wireless Network Topologies Segmentation (Market Size & Forecast: USD billion, 2024 – 2030) |
|
8.1 Topology Type |
|
8.1.1 Point-to-Point (P2P) |
|
8.1.2 Point-to-Multipoint (P2MP) |
|
8.1.3 Mesh Network |
|
8.1.4 Star Topology |
|
8.1.5 Tree Topology |
|
8.1.6 Hybrid Topologies |
|
8.2 Technology |
|
8.2.1 Wi-Fi |
|
8.2.2 Bluetooth |
|
8.2.3 Zigbee |
|
8.2.4 Cellular |
|
8.2.5 Others |
|
8.3 End-Use Industry |
|
8.3.1 Telecommunications |
|
8.3.2 Information Technology |
|
8.3.3 Healthcare |
|
8.3.4 Transportation |
|
8.3.5 Others |
|
8.4 Enterprise size |
|
8.4.1 Large Enterprises |
|
8.4.2 Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) |
|
8.5 Deployment Mode |
|
8.5.1 Cloud-based |
|
8.5.2 On-premises |
|
8.6 Application |
|
8.6.1 Consumer Electronics |
|
8.6.2 Industrial Automation |
|
8.6.3 Internet of Things (IoT) |
|
8.6.4 Remote Monitoring and Sensing |
|
8.6.5 Communication and Networking |
|
8.6.6 Others |
|
8.7 Country |
|
8.7.1 United Kingdom |
|
8.7.1.1 Topology Type |
|
8.7.1.1.1 Point-to-Point (P2P) |
|
8.7.1.1.2 Point-to-Multipoint (P2MP) |
|
8.7.1.1.3 Mesh Network |
|
8.7.1.1.4 Star Topology |
|
8.7.1.1.5 Tree Topology |
|
8.7.1.1.6 Hybrid Topologies |
|
8.7.1.2 Technology |
|
8.7.1.2.1 Wifi |
|
8.7.1.2.2 Bluetooth |
|
8.7.1.2.3 Zigbee |
|
8.7.1.2.4 Cellular |
|
8.7.1.2.5 Others |
|
8.7.1.3 End-Use Industry |
|
8.7.1.3.1 Telecommunications |
|
8.7.1.3.2 Information Technology |
|
8.7.1.3.3 Healthcare |
|
8.7.1.3.4 Transportation |
|
8.7.1.3.4 Others |
|
8.7.1.4 Enterprise size |
|
8.7.1.4.1 Large Enterprises |
|
8.7.1.4.2 Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) |
|
8.7.1.5 Deployment Mode |
|
8.7.1.5.1 Cloud-based |
|
8.7.1.5.2 On-premises |
|
8.7.1.6 Application |
|
8.7.1.6.1 Consumer Electronics |
|
8.7.1.6.2 Industrial Automation |
|
8.7.1.6.3 Internet of Things (IoT) |
|
8.7.1.6.4 Remote Monitoring and Sensing |
|
8.7.1.6.5 Communication and Networking |
|
8.7.1.6.6 Others |
|
8.7.2 France |
|
8.7.2.1 Topology Type |
|
8.7.2.1.1 Point-to-Point (P2P) |
|
8.7.2.1.2 Point-to-Multipoint (P2MP) |
|
8.7.2.1.3 Mesh Network |
|
8.7.2.1.4 Star Topology |
|
8.7.2.1.5 Tree Topology |
|
8.7.2.1.6 Hybrid Topologies |
|
8.7.2.2 Technology |
|
8.7.2.2.1 Wifi |
|
8.7.2.2.2 Bluetooth |
|
8.7.2.2.3 Zigbee |
|
8.7.2.2.4 Cellular |
|
8.7.2.2.5 Others |
|
8.7.2.3 End-Use Industry |
|
8.7.2.3.1 Telecommunications |
|
8.7.2.3.2 Information Technology |
|
8.7.2.3.3 Healthcare |
|
8.7.2.3.4 Transportation |
|
8.7.2.3.4 Others |
|
8.7.2.4 Enterprise size |
|
8.7.2.4.1 Large Enterprises |
|
8.7.2.4.2 Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) |
|
8.7.2.5 Deployment Mode |
|
8.7.2.5.1 Cloud-based |
|
8.7.2.5.2 On-premises |
|
8.7.2.6 Application |
|
8.7.2.6.1 Consumer Electronics |
|
8.7.2.6.2 Industrial Automation |
|
8.7.2.6.3 Internet of Things (IoT) |
|
8.7.2.6.4 Remote Monitoring and Sensing |
|
8.7.2.6.5 Communication and Networking |
|
8.7.2.6.6 Others |
|
8.7.3 Germany |
|
8.7.3.1 Topology Type |
|
8.7.3.1.1 Point-to-Point (P2P) |
|
8.7.3.1.2 Point-to-Multipoint (P2MP) |
|
8.7.3.1.3 Mesh Network |
|
8.7.3.1.4 Star Topology |
|
8.7.3.1.5 Tree Topology |
|
8.7.3.1.6 Hybrid Topologies |
|
8.7.3.2 Technology |
|
8.7.3.2.1 Wifi |
|
8.7.3.2.2 Bluetooth |
|
8.7.3.2.3 Zigbee |
|
8.7.3.2.4 Cellular |
|
8.7.3.2.5 Others |
|
8.7.3.3 End-Use Industry |
|
8.7.3.3.1 Telecommunications |
|
8.7.3.3.2 Information Technology |
|
8.7.3.3.3 Healthcare |
|
8.7.3.3.4 Transportation |
|
8.7.3.3.4 Others |
|
8.7.3.4 Enterprise size |
|
8.7.3.4.1 Large Enterprises |
|
8.7.3.4.2 Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) |
|
8.7.3.5 Deployment Mode |
|
8.7.3.5.1 Cloud-based |
|
8.7.3.5.2 On-premises |
|
8.7.3.6 Application |
|
8.7.3.6.1 Consumer Electronics |
|
8.7.3.6.2 Industrial Automation |
|
8.7.3.6.3 Internet of Things (IoT) |
|
8.7.3.6.4 Remote Monitoring and Sensing |
|
8.7.3.6.5 Communication and Networking |
|
8.7.3.6.6 Others |
|
8.7.4 Italy |
|
8.7.4.1 Topology Type |
|
8.7.4.1.1 Point-to-Point (P2P) |
|
8.7.4.1.2 Point-to-Multipoint (P2MP) |
|
8.7.4.1.3 Mesh Network |
|
8.7.4.1.4 Star Topology |
|
8.7.4.1.5 Tree Topology |
|
8.7.4.1.6 Hybrid Topologies |
|
8.7.4.2 Technology |
|
8.7.4.2.1 Wifi |
|
8.7.4.2.2 Bluetooth |
|
8.7.4.2.3 Zigbee |
|
8.7.4.2.4 Cellular |
|
8.7.4.2.5 Others |
|
8.7.4.3 End-Use Industry |
|
8.7.4.3.1 Telecommunications |
|
8.7.4.3.2 Information Technology |
|
8.7.4.3.3 Healthcare |
|
8.7.4.3.4 Transportation |
|
8.7.4.3.4 Others |
|
8.7.4.4 Enterprise size |
|
8.7.4.4.1 Large Enterprises |
|
8.7.4.4.2 Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) |
|
8.7.4.5 Deployment Mode |
|
8.7.4.5.1 Cloud-based |
|
8.7.4.5.2 On-premises |
|
8.7.4.6 Application |
|
8.7.4.6.1 Consumer Electronics |
|
8.7.4.6.2 Industrial Automation |
|
8.7.4.6.3 Internet of Things (IoT) |
|
8.7.4.6.4 Remote Monitoring and Sensing |
|
8.7.4.6.5 Communication and Networking |
|
8.7.4.6.6 Others |
|
8.7.5 Rest of Europe |
|
8.7.5.1 Topology Type |
|
8.7.5.1.1 Point-to-Point (P2P) |
|
8.7.5.1.2 Point-to-Multipoint (P2MP) |
|
8.7.5.1.3 Mesh Network |
|
8.7.5.1.4 Star Topology |
|
8.7.5.1.5 Tree Topology |
|
8.7.5.1.6 Hybrid Topologies |
|
8.7.5.2 Technology |
|
8.7.5.2.1 Wifi |
|
8.7.5.2.2 Bluetooth |
|
8.7.5.2.3 Zigbee |
|
8.7.5.2.4 Cellular |
|
8.7.5.2.5 Others |
|
8.7.5.3 End-Use Industry |
|
8.7.5.3.1 Telecommunications |
|
8.7.5.3.2 Information Technology |
|
8.7.5.3.3 Healthcare |
|
8.7.5.3.4 Transportation |
|
8.7.5.3.4 Others |
|
8.7.5.4 Enterprise size |
|
8.7.5.4.1 Large Enterprises |
|
8.7.5.4.2 Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) |
|
8.7.5.5 Deployment Mode |
|
8.7.5.5.1 Cloud-based |
|
8.7.5.5.2 On-premises |
|
8.7.5.6 Application |
|
8.7.5.6.1 Consumer Electronics |
|
8.7.5.6.2 Industrial Automation |
|
8.7.5.6.3 Internet of Things (IoT) |
|
8.7.5.6.4 Remote Monitoring and Sensing |
|
8.7.5.6.5 Communication and Networking |
|
8.7.5.6.6 Others |
|
9. Asia Pacific Wireless Network Topologies Market Segmentation (Market Size & Forecast: USD billion, 2024 – 2030) |
|
9.1 Topology Type |
|
9.1.1 Point-to-Point (P2P) |
|
9.1.2 Point-to-Multipoint (P2MP) |
|
9.1.3 Mesh Network |
|
9.1.4 Star Topology |
|
9.1.5 Tree Topology |
|
9.1.6 Hybrid Topologies |
|
9.2 Technology |
|
9.2.1 Wi-Fi |
|
9.2.2 Bluetooth |
|
9.2.3 Zigbee |
|
9.2.4 Cellular |
|
9.2.5 Others |
|
9.3 End-Use Industry |
|
9.3.1 Telecommunications |
|
9.3.2 Information Technology |
|
9.3.3 Healthcare |
|
9.3.4 Transportation |
|
9.3.5 Others |
|
9.4 Enterprise size |
|
9.4.1 Large Enterprises |
|
9.4.2 Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) |
|
9.5 Deployment Mode |
|
9.5.1 Cloud-based |
|
9.5.2 On-premises |
|
9.6 Application |
|
9.6.1 Consumer Electronics |
|
9.6.2 Industrial Automation |
|
9.6.3 Internet of Things (IoT) |
|
9.6.4 Remote Monitoring and Sensing |
|
9.6.5 Communication and Networking |
|
9.6.6 Others |
|
9.7 Country |
|
9.7.1 China |
|
9.7.1.1 Topology Type |
|
9.7.1.1.1 Point-to-Point (P2P) |
|
9.7.1.1.2 Point-to-Multipoint (P2MP) |
|
9.7.1.1.3 Mesh Network |
|
9.7.1.1.4 Star Topology |
|
9.7.1.1.5 Tree Topology |
|
9.7.1.1.6 Hybrid Topologies |
|
9.7.1.2 Technology |
|
9.7.1.2.1 Wifi |
|
9.7.1.2.2 Bluetooth |
|
9.7.1.2.3 Zigbee |
|
9.7.1.2.4 Cellular |
|
9.7.1.2.5 Others |
|
9.7.1.3 End-Use Industry |
|
9.7.1.3.1 Telecommunications |
|
9.7.1.3.2 Information Technology |
|
9.7.1.3.3 Healthcare |
|
9.7.1.3.4 Transportation |
|
9.7.1.3.4 Others |
|
9.7.1.4 Enterprise size |
|
9.7.1.4.1 Large Enterprises |
|
9.7.1.4.2 Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) |
|
9.7.1.5 Deployment Mode |
|
9.7.1.5.1 Cloud-based |
|
9.7.1.5.2 On-premises |
|
9.7.1.6 Application |
|
9.7.1.6.1 Consumer Electronics |
|
9.7.1.6.2 Industrial Automation |
|
9.7.1.6.3 Internet of Things (IoT) |
|
9.7.1.6.4 Remote Monitoring and Sensing |
|
9.7.1.6.5 Communication and Networking |
|
9.7.1.6.6 Others |
|
9.7.2 Japan |
|
9.7.2.1 Topology Type |
|
9.7.2.1.1 Point-to-Point (P2P) |
|
9.7.2.1.2 Point-to-Multipoint (P2MP) |
|
9.7.2.1.3 Mesh Network |
|
9.7.2.1.4 Star Topology |
|
9.7.2.1.5 Tree Topology |
|
9.7.2.1.6 Hybrid Topologies |
|
9.7.2.2 Technology |
|
9.7.2.2.1 Wifi |
|
9.7.2.2.2 Bluetooth |
|
9.7.2.2.3 Zigbee |
|
9.7.2.2.4 Cellular |
|
9.7.2.2.5 Others |
|
9.7.2.3 End-Use Industry |
|
9.7.2.3.1 Telecommunications |
|
9.7.2.3.2 Information Technology |
|
9.7.2.3.3 Healthcare |
|
9.7.2.3.4 Transportation |
|
9.7.2.3.4 Others |
|
9.7.2.4 Enterprise size |
|
9.7.2.4.1 Large Enterprises |
|
9.7.2.4.2 Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) |
|
9.7.2.5 Deployment Mode |
|
9.7.2.5.1 Cloud-based |
|
9.7.2.5.2 On-premises |
|
9.7.2.6 Application |
|
9.7.2.6.1 Consumer Electronics |
|
9.7.2.6.2 Industrial Automation |
|
9.7.2.6.3 Internet of Things (IoT) |
|
9.7.2.6.4 Remote Monitoring and Sensing |
|
9.7.2.6.5 Communication and Networking |
|
9.7.2.6.6 Others |
|
9.7.3 India |
|
9.7.3.1 Topology Type |
|
9.7.3.1.1 Point-to-Point (P2P) |
|
9.7.3.1.2 Point-to-Multipoint (P2MP) |
|
9.7.3.1.3 Mesh Network |
|
9.7.3.1.4 Star Topology |
|
9.7.3.1.5 Tree Topology |
|
9.7.3.1.6 Hybrid Topologies |
|
9.7.3.2 Technology |
|
9.7.3.2.1 Wifi |
|
9.7.3.2.2 Bluetooth |
|
9.7.3.2.3 Zigbee |
|
9.7.3.2.4 Cellular |
|
9.7.3.2.5 Others |
|
9.7.3.3 End-Use Industry |
|
9.7.3.3.1 Telecommunications |
|
9.7.3.3.2 Information Technology |
|
9.7.3.3.3 Healthcare |
|
9.7.3.3.4 Transportation |
|
9.7.3.3.4 Others |
|
9.7.3.4 Enterprise size |
|
9.7.3.4.1 Large Enterprises |
|
9.7.3.4.2 Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) |
|
9.7.3.5 Deployment Mode |
|
9.7.3.5.1 Cloud-based |
|
9.7.3.5.2 On-premises |
|
9.7.3.6 Application |
|
9.7.3.6.1 Consumer Electronics |
|
9.7.3.6.2 Industrial Automation |
|
9.7.3.6.3 Internet of Things (IoT) |
|
9.7.3.6.4 Remote Monitoring and Sensing |
|
9.7.3.6.5 Communication and Networking |
|
9.7.3.6.6 Others |
|
9.7.4 South Korea |
|
9.7.4.1 Topology Type |
|
9.7.4.1.1 Point-to-Point (P2P) |
|
9.7.4.1.2 Point-to-Multipoint (P2MP) |
|
9.7.4.1.3 Mesh Network |
|
9.7.4.1.4 Star Topology |
|
9.7.4.1.5 Tree Topology |
|
9.7.4.1.6 Hybrid Topologies |
|
9.7.4.2 Technology |
|
9.7.4.2.1 Wifi |
|
9.7.4.2.2 Bluetooth |
|
9.7.4.2.3 Zigbee |
|
9.7.4.2.4 Cellular |
|
9.7.4.2.5 Others |
|
9.7.4.3 End-Use Industry |
|
9.7.4.3.1 Telecommunications |
|
9.7.4.3.2 Information Technology |
|
9.7.4.3.3 Healthcare |
|
9.7.4.3.4 Transportation |
|
9.7.4.3.4 Others |
|
9.7.4.4 Enterprise size |
|
9.7.4.4.1 Large Enterprises |
|
9.7.4.4.2 Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) |
|
9.7.4.5 Deployment Mode |
|
9.7.4.5.1 Cloud-based |
|
9.7.4.5.2 On-premises |
|
9.7.4.6 Application |
|
9.7.4.6.1 Consumer Electronics |
|
9.7.4.6.2 Industrial Automation |
|
9.7.4.6.3 Internet of Things (IoT) |
|
9.7.4.6.4 Remote Monitoring and Sensing |
|
9.7.4.6.5 Communication and Networking |
|
9.7.4.6.6 Others |
|
9.7.5 Rest of Asia Pacific |
|
9.7.5.1 Topology Type |
|
9.7.5.1.1 Point-to-Point (P2P) |
|
9.7.5.1.2 Point-to-Multipoint (P2MP) |
|
9.7.5.1.3 Mesh Network |
|
9.7.5.1.4 Star Topology |
|
9.7.5.1.5 Tree Topology |
|
9.7.5.1.6 Hybrid Topologies |
|
9.7.5.2 Technology |
|
9.7.5.2.1 Wifi |
|
9.7.5.2.2 Bluetooth |
|
9.7.5.2.3 Zigbee |
|
9.7.5.2.4 Cellular |
|
9.7.5.2.5 Others |
|
9.7.5.3 End-Use Industry |
|
9.7.5.3.1 Telecommunications |
|
9.7.5.3.2 Information Technology |
|
9.7.5.3.3 Healthcare |
|
9.7.5.3.4 Transportation |
|
9.7.5.3.4 Others |
|
9.7.5.4 Enterprise size |
|
9.7.5.4.1 Large Enterprises |
|
9.7.5.4.2 Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) |
|
9.7.5.5 Deployment Mode |
|
9.7.5.5.1 Cloud-based |
|
9.7.5.5.2 On-premises |
|
9.7.5.6 Application |
|
9.7.5.6.1 Consumer Electronics |
|
9.7.5.6.2 Industrial Automation |
|
9.7.5.6.3 Internet of Things (IoT) |
|
9.7.5.6.4 Remote Monitoring and Sensing |
|
9.7.5.6.5 Communication and Networking |
|
9.7.5.6.6 Others |
|
10. Latin America Wireless Network Topologies Market Segmentation (Market Size & Forecast: USD billion, 2024 – 2030) |
|
10.1 Topology Type |
|
10.1.1 Point-to-Point (P2P) |
|
10.1.2 Point-to-Multipoint (P2MP) |
|
10.1.3 Mesh Network |
|
10.1.4 Star Topology |
|
10.1.5 Tree Topology |
|
10.1.6 Hybrid Topologies |
|
10.2 Technology |
|
10.2.1 Wi-Fi |
|
10.2.2 Bluetooth |
|
10.2.3 Zigbee |
|
10.2.4 Cellular |
|
10.2.5 Others |
|
10.3 End-Use Industry |
|
10.3.1 Telecommunications |
|
10.3.2 Information Technology |
|
10.3.3 Healthcare |
|
10.3.4 Transportation |
|
10.3.5 Others |
|
10.4 Enterprise size |
|
10.4.1 Large Enterprises |
|
10.4.2 Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) |
|
10.5 Deployment Mode |
|
10.5.1 Cloud-based |
|
10.5.2 On-premises |
|
10.6 Application |
|
10.6.1 Consumer Electronics |
|
10.6.2 Industrial Automation |
|
10.6.3 Internet of Things (IoT) |
|
10.6.4 Remote Monitoring and Sensing |
|
10.6.5 Communication and Networking |
|
10.6.6 Others |
|
10.7 Country |
|
10.7.1 Brazil |
|
10.7.1.1 Topology Type |
|
10.7.1.1.1 Point-to-Point (P2P) |
|
10.7.1.1.2 Point-to-Multipoint (P2MP) |
|
10.7.1.1.3 Mesh Network |
|
10.7.1.1.4 Star Topology |
|
10.7.1.1.5 Tree Topology |
|
10.7.1.1.6 Hybrid Topologies |
|
10.7.1.2 Technology |
|
10.7.1.2.1 Wifi |
|
10.7.1.2.2 Bluetooth |
|
10.7.1.2.3 Zigbee |
|
10.7.1.2.4 Cellular |
|
10.7.1.2.5 Others |
|
10.7.1.3 End-Use Industry |
|
10.7.1.3.1 Telecommunications |
|
10.7.1.3.2 Information Technology |
|
10.7.1.3.3 Healthcare |
|
10.7.1.3.4 Transportation |
|
10.7.1.3.4 Others |
|
10.7.1.4 Enterprise size |
|
10.7.1.4.1 Large Enterprises |
|
10.7.1.4.2 Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) |
|
10.7.1.5 Deployment Mode |
|
10.7.1.5.1 Cloud-based |
|
10.7.1.5.2 On-premises |
|
10.7.1.6 Application |
|
10.7.1.6.1 Consumer Electronics |
|
10.7.1.6.2 Industrial Automation |
|
10.7.1.6.3 Internet of Things (IoT) |
|
10.7.1.6.4 Remote Monitoring and Sensing |
|
10.7.1.6.5 Communication and Networking |
|
10.7.1.6.6 Others |
|
10.7.2 Mexico |
|
10.7.2.1 Topology Type |
|
10.7.2.1.1 Point-to-Point (P2P) |
|
10.7.2.1.2 Point-to-Multipoint (P2MP) |
|
10.7.2.1.3 Mesh Network |
|
10.7.2.1.4 Star Topology |
|
10.7.2.1.5 Tree Topology |
|
10.7.2.1.6 Hybrid Topologies |
|
10.7.2.2 Technology |
|
10.7.2.2.1 Wifi |
|
10.7.2.2.2 Bluetooth |
|
10.7.2.2.3 Zigbee |
|
10.7.2.2.4 Cellular |
|
10.7.2.2.5 Others |
|
10.7.2.3 End-Use Industry |
|
10.7.2.3.1 Telecommunications |
|
10.7.2.3.2 Information Technology |
|
10.7.2.3.3 Healthcare |
|
10.7.2.3.4 Transportation |
|
10.7.2.3.4 Others |
|
10.7.2.4 Enterprise size |
|
10.7.2.4.1 Large Enterprises |
|
10.7.2.4.2 Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) |
|
10.7.2.5 Deployment Mode |
|
10.7.2.5.1 Cloud-based |
|
10.7.2.5.2 On-premises |
|
10.7.2.6 Application |
|
10.7.2.6.1 Consumer Electronics |
|
10.7.2.6.2 Industrial Automation |
|
10.7.2.6.3 Internet of Things (IoT) |
|
10.7.2.6.4 Remote Monitoring and Sensing |
|
10.7.2.6.5 Communication and Networking |
|
10.7.2.6.6 Others |
|
10.7.3 Argentina |
|
10.7.3.1 Topology Type |
|
10.7.3.1.1 Point-to-Point (P2P) |
|
10.7.3.1.2 Point-to-Multipoint (P2MP) |
|
10.7.3.1.3 Mesh Network |
|
10.7.3.1.4 Star Topology |
|
10.7.3.1.5 Tree Topology |
|
10.7.3.1.6 Hybrid Topologies |
|
10.7.3.2 Technology |
|
10.7.3.2.1 Wifi |
|
10.7.3.2.2 Bluetooth |
|
10.7.3.2.3 Zigbee |
|
10.7.3.2.4 Cellular |
|
10.7.3.2.5 Others |
|
10.7.3.3 End-Use Industry |
|
10.7.3.3.1 Telecommunications |
|
10.7.3.3.2 Information Technology |
|
10.7.3.3.3 Healthcare |
|
10.7.3.3.4 Transportation |
|
10.7.3.3.4 Others |
|
10.7.3.4 Enterprise size |
|
10.7.3.4.1 Large Enterprises |
|
10.7.3.4.2 Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) |
|
10.7.3.5 Deployment Mode |
|
10.7.3.5.1 Cloud-based |
|
10.7.3.5.2 On-premises |
|
10.7.3.6 Application |
|
10.7.3.6.1 Consumer Electronics |
|
10.7.3.6.2 Industrial Automation |
|
10.7.3.6.3 Internet of Things (IoT) |
|
10.7.3.6.4 Remote Monitoring and Sensing |
|
10.7.3.6.5 Communication and Networking |
|
10.7.3.6.6 Others |
|
10.7.4 Rest of Latin America |
|
10.7.4.1 Topology Type |
|
10.7.4.1.1 Point-to-Point (P2P) |
|
10.7.4.1.2 Point-to-Multipoint (P2MP) |
|
10.7.4.1.3 Mesh Network |
|
10.7.4.1.4 Star Topology |
|
10.7.4.1.5 Tree Topology |
|
10.7.4.1.6 Hybrid Topologies |
|
10.7.4.2 Technology |
|
10.7.4.2.1 Wifi |
|
10.7.4.2.2 Bluetooth |
|
10.7.4.2.3 Zigbee |
|
10.7.4.2.4 Cellular |
|
10.7.4.2.5 Others |
|
10.7.4.3 End-Use Industry |
|
10.7.4.3.1 Telecommunications |
|
10.7.4.3.2 Information Technology |
|
10.7.4.3.3 Healthcare |
|
10.7.4.3.4 Transportation |
|
10.7.4.3.4 Others |
|
10.7.4.4 Enterprise size |
|
10.7.4.4.1 Large Enterprises |
|
10.7.4.4.2 Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) |
|
10.7.4.5 Deployment Mode |
|
10.7.4.5.1 Cloud-based |
|
10.7.4.5.2 On-premises |
|
10.7.4.6 Application |
|
10.7.4.6.1 Consumer Electronics |
|
10.7.4.6.2 Industrial Automation |
|
10.7.4.6.3 Internet of Things (IoT) |
|
10.7.4.6.4 Remote Monitoring and Sensing |
|
10.7.4.6.5 Communication and Networking |
|
10.7.4.6.6 Others |
|
11. Middle East & Africa Wireless Network Topologies Market Segmentation (Market Size & Forecast: USD billion, 2024 – 2030) |
|
11.1 Topology Type |
|
11.1.1 Point-to-Point (P2P) |
|
11.1.2 Point-to-Multipoint (P2MP) |
|
11.1.3 Mesh Network |
|
11.1.4 Star Topology |
|
11.1.5 Tree Topology |
|
11.1.6 Hybrid Topologies |
|
11.2 Technology |
|
11.2.1 Wi-Fi |
|
11.2.2 Bluetooth |
|
11.2.3 Zigbee |
|
11.2.4 Cellular |
|
11.2.5 Others |
|
11.3 End-Use Industry |
|
11.3.1 Telecommunications |
|
11.3.2 Information Technology |
|
11.3.3 Healthcare |
|
11.3.4 Transportation |
|
11.3.5 Others |
|
11.4 Enterprise size |
|
11.4.1 Large Enterprises |
|
11.4.2 Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) |
|
11.5 Deployment Mode |
|
11.5.1 Cloud-based |
|
11.5.2 On-premises |
|
11.6 Application |
|
11.6.1 Consumer Electronics |
|
11.6.2 Industrial Automation |
|
11.6.3 Internet of Things (IoT) |
|
11.6.4 Remote Monitoring and Sensing |
|
11.6.5 Communication and Networking |
|
11.6.6 Others |
|
11.7 Country |
|
11.7.1 Saudi Arabia |
|
11.7.1.1 Topology Type |
|
11.7.1.1.1 Point-to-Point (P2P) |
|
11.7.1.1.2 Point-to-Multipoint (P2MP) |
|
11.7.1.1.3 Mesh Network |
|
11.7.1.1.4 Star Topology |
|
11.7.1.1.5 Tree Topology |
|
11.7.1.1.6 Hybrid Topologies |
|
11.7.1.2 Technology |
|
11.7.1.2.1 Wifi |
|
11.7.1.2.2 Bluetooth |
|
11.7.1.2.3 Zigbee |
|
11.7.1.2.4 Cellular |
|
11.7.1.2.5 Others |
|
11.7.1.3 End-Use Industry |
|
11.7.1.3.1 Telecommunications |
|
11.7.1.3.2 Information Technology |
|
11.7.1.3.3 Healthcare |
|
11.7.1.3.4 Transportation |
|
11.7.1.3.4 Others |
|
11.7.1.4 Enterprise size |
|
11.7.1.4.1 Large Enterprises |
|
11.7.1.4.2 Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) |
|
11.7.1.5 Deployment Mode |
|
11.7.1.5.1 Cloud-based |
|
11.7.1.5.2 On-premises |
|
11.7.1.6 Application |
|
11.7.1.6.1 Consumer Electronics |
|
11.7.1.6.2 Industrial Automation |
|
11.7.1.6.3 Internet of Things (IoT) |
|
11.7.1.6.4 Remote Monitoring and Sensing |
|
11.7.1.6.5 Communication and Networking |
|
11.7.1.6.6 Others |
|
11.7.2 South Africa |
|
11.7.2.1 Topology Type |
|
11.7.2.1.1 Point-to-Point (P2P) |
|
11.7.2.1.2 Point-to-Multipoint (P2MP) |
|
11.7.2.1.3 Mesh Network |
|
11.7.2.1.4 Star Topology |
|
11.7.2.1.5 Tree Topology |
|
11.7.2.1.6 Hybrid Topologies |
|
11.7.2.2 Technology |
|
11.7.2.2.1 Wifi |
|
11.7.2.2.2 Bluetooth |
|
11.7.2.2.3 Zigbee |
|
11.7.2.2.4 Cellular |
|
11.7.2.2.5 Others |
|
11.7.2.3 End-Use Industry |
|
11.7.2.3.1 Telecommunications |
|
11.7.2.3.2 Information Technology |
|
11.7.2.3.3 Healthcare |
|
11.7.2.3.4 Transportation |
|
11.7.2.3.4 Others |
|
11.7.2.4 Enterprise size |
|
11.7.2.4.1 Large Enterprises |
|
11.7.2.4.2 Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) |
|
11.7.2.5 Deployment Mode |
|
11.7.2.5.1 Cloud-based |
|
11.7.2.5.2 On-premises |
|
11.7.2.6 Application |
|
11.7.2.6.1 Consumer Electronics |
|
11.7.2.6.2 Industrial Automation |
|
11.7.2.6.3 Internet of Things (IoT) |
|
11.7.2.6.4 Remote Monitoring and Sensing |
|
11.7.2.6.5 Communication and Networking |
|
11.7.2.6.6 Others |
|
11.7.3 United Arab Emirates |
|
11.7.3.1 Topology Type |
|
11.7.3.1.1 Point-to-Point (P2P) |
|
11.7.3.1.2 Point-to-Multipoint (P2MP) |
|
11.7.3.1.3 Mesh Network |
|
11.7.3.1.4 Star Topology |
|
11.7.3.1.5 Tree Topology |
|
11.7.3.1.6 Hybrid Topologies |
|
11.7.3.2 Technology |
|
11.7.3.2.1 Wifi |
|
11.7.3.2.2 Bluetooth |
|
11.7.3.2.3 Zigbee |
|
11.7.3.2.4 Cellular |
|
11.7.3.2.5 Others |
|
11.7.3.3 End-Use Industry |
|
11.7.3.3.1 Telecommunications |
|
11.7.3.3.2 Information Technology |
|
11.7.3.3.3 Healthcare |
|
11.7.3.3.4 Transportation |
|
11.7.3.3.4 Others |
|
11.7.3.4 Enterprise size |
|
11.7.3.4.1 Large Enterprises |
|
11.7.3.4.2 Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) |
|
11.7.3.5 Deployment Mode |
|
11.7.3.5.1 Cloud-based |
|
11.7.3.5.2 On-premises |
|
11.7.3.6 Application |
|
11.7.3.6.1 Consumer Electronics |
|
11.7.3.6.2 Industrial Automation |
|
11.7.3.6.3 Internet of Things (IoT) |
|
11.7.3.6.4 Remote Monitoring and Sensing |
|
11.7.3.6.5 Communication and Networking |
|
11.7.3.6.6 Others |
|
11.7.4 Rest of Middle East & Africa |
|
11.7.4.1 Topology Type |
|
11.7.4.1.1 Point-to-Point (P2P) |
|
11.7.4.1.2 Point-to-Multipoint (P2MP) |
|
11.7.4.1.3 Mesh Network |
|
11.7.4.1.4 Star Topology |
|
11.7.4.1.5 Tree Topology |
|
11.7.4.1.6 Hybrid Topologies |
|
11.7.4.2 Technology |
|
11.7.4.2.1 Wifi |
|
11.7.4.2.2 Bluetooth |
|
11.7.4.2.3 Zigbee |
|
11.7.4.2.4 Cellular |
|
11.7.4.2.5 Others |
|
11.7.4.3 End-Use Industry |
|
11.7.4.3.1 Telecommunications |
|
11.7.4.3.2 Information Technology |
|
11.7.4.3.3 Healthcare |
|
11.7.4.3.4 Transportation |
|
11.7.4.3.4 Others |
|
11.7.4.4 Enterprise size |
|
11.7.4.4.1 Large Enterprises |
|
11.7.4.4.2 Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) |
|
11.7.4.5 Deployment Mode |
|
11.7.4.5.1 Cloud-based |
|
11.7.4.5.2 On-premises |
|
11.7.4.6 Application |
|
11.7.4.6.1 Consumer Electronics |
|
11.7.4.6.2 Industrial Automation |
|
11.7.4.6.3 Internet of Things (IoT) |
|
11.7.4.6.4 Remote Monitoring and Sensing |
|
11.7.4.6.5 Communication and Networking |
|
11.7.4.6.6 Others |
|
12. Competitive Landscape |
|
12.1 Company Market Share Analysis |
|
12.2 Competitive Matrix |
|
12.2 Product Benchmarking |
|
12.3 Company Profiles (Manufacturers of Wireless Network Topologies) |
|
12.3.1 Cisco Systems |
|
12.3.1.1 Company Synopsis |
|
12.3.1.2 Company Financials |
|
12.3.1.3 Product/ Service Portfolio |
|
12.3.1.4 Recent Developments |
|
12.3.2 Aruba Networks (a Hewlett Packard Enterprise company) |
|
12.3.3 Ericsson |
|
12.3.4 Huawei Technologies |
|
12.3.5 Nokia Networks |
|
12.3.6 Samsung Networks |
|
12.3.7 ZTE Corporation |
|
12.3.8 Qualcomm Technologies |
|
12.3.9 Nordic Semiconductor |
|
12.3.10 Ubiquiti Networks |
|
12.3.11 TP-Link Technologies |
|
12.3.12 NETGEAR |
|
12.4 Company Profiles (Demand Side) |
|
12.4.1 AT&T |
|
12.4.1.1 Company Synopsis |
|
12.3.1.2 Company Financials |
|
12.3.1.3 Product/ Service Portfolio |
|
12.3.1.4 Recent Developments |
|
12.4.2 Verizon |
|
12.4.3 UPS |
|
12.4.4 FedEx |
|
12.4.5 Schneider Electric |
|
13. Analyst Recommendations |
Let us connect with you TOC
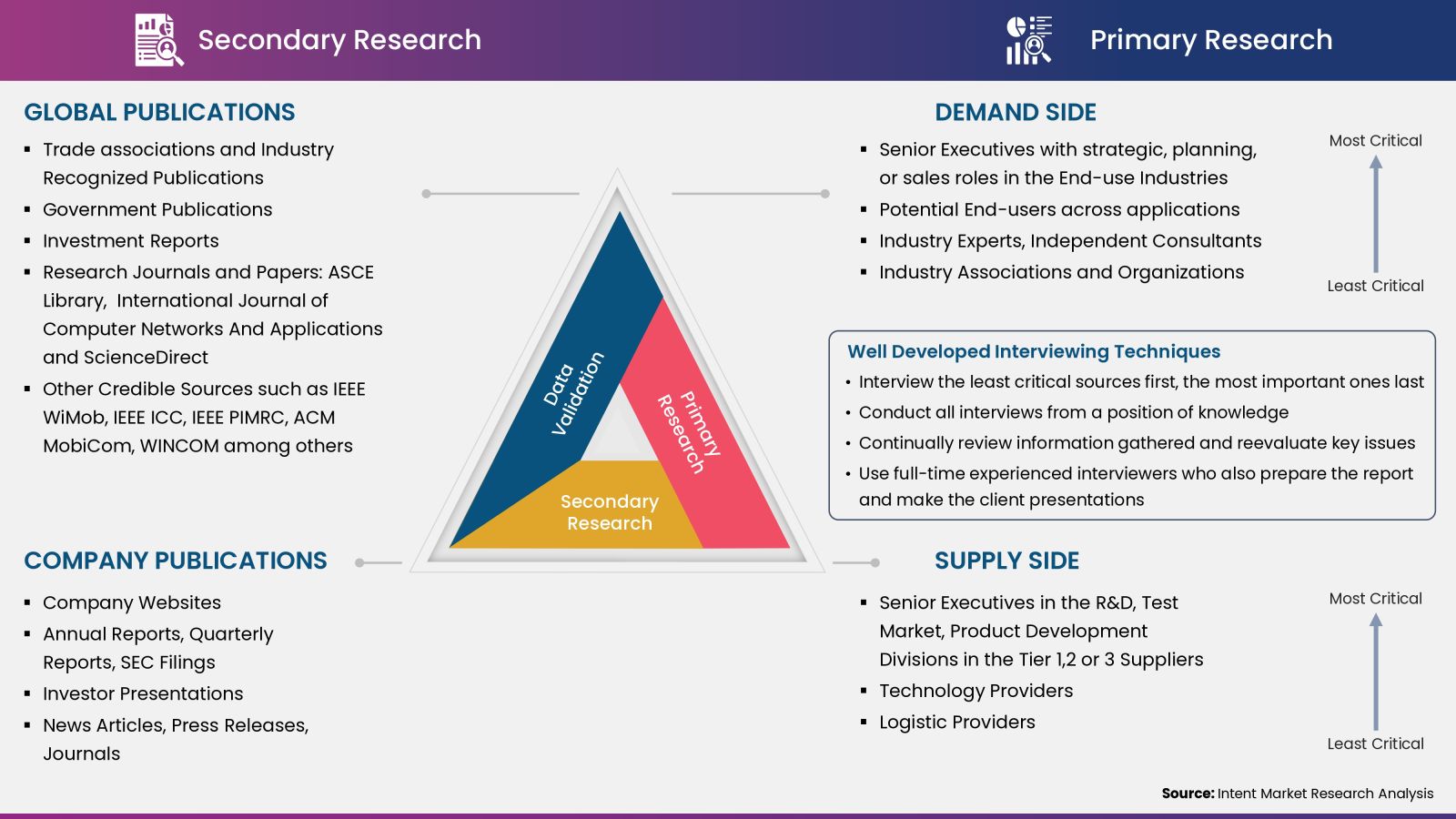
Intent Market Research employs a rigorous methodology to minimize residual errors by carefully defining the scope, validating findings through primary research, and consistently updating our in-house database. This dynamic approach allows us to capture ongoing market fluctuations and adapt to evolving market uncertainties.
The research factors used in our methodology vary depending on the specific market being analyzed. To begin with, we incorporate both demand and supply side information into our model to identify and address market gaps. Additionally, we also employ approaches such as Macro-indicator Analysis, Factor Analysis, Value Chain-Based Sizing, and forecasting to further increase the accuracy of the numbers and validate the findings.
Research Approach

- Secondary Research Approach: During the initial phase of the research process, we acquire and accumulate extensive data continuously. This data is carefully filtered and validated through a variety of secondary sources.
- Primary Research Approach: Following the consolidation of data gathered through secondary research, we initiate a validation process to verify all the market numbers, and assumptions and validate the findings by engaging with subject matter experts.
Data Collection, Analysis and Interpretation:
Research Methodology
Our market research methodology utilizes both top-down and bottom-up approaches to segment and estimate quantitative aspects of the market. We also employ multi-perspective analysis, examining the market from distinct viewpoints.
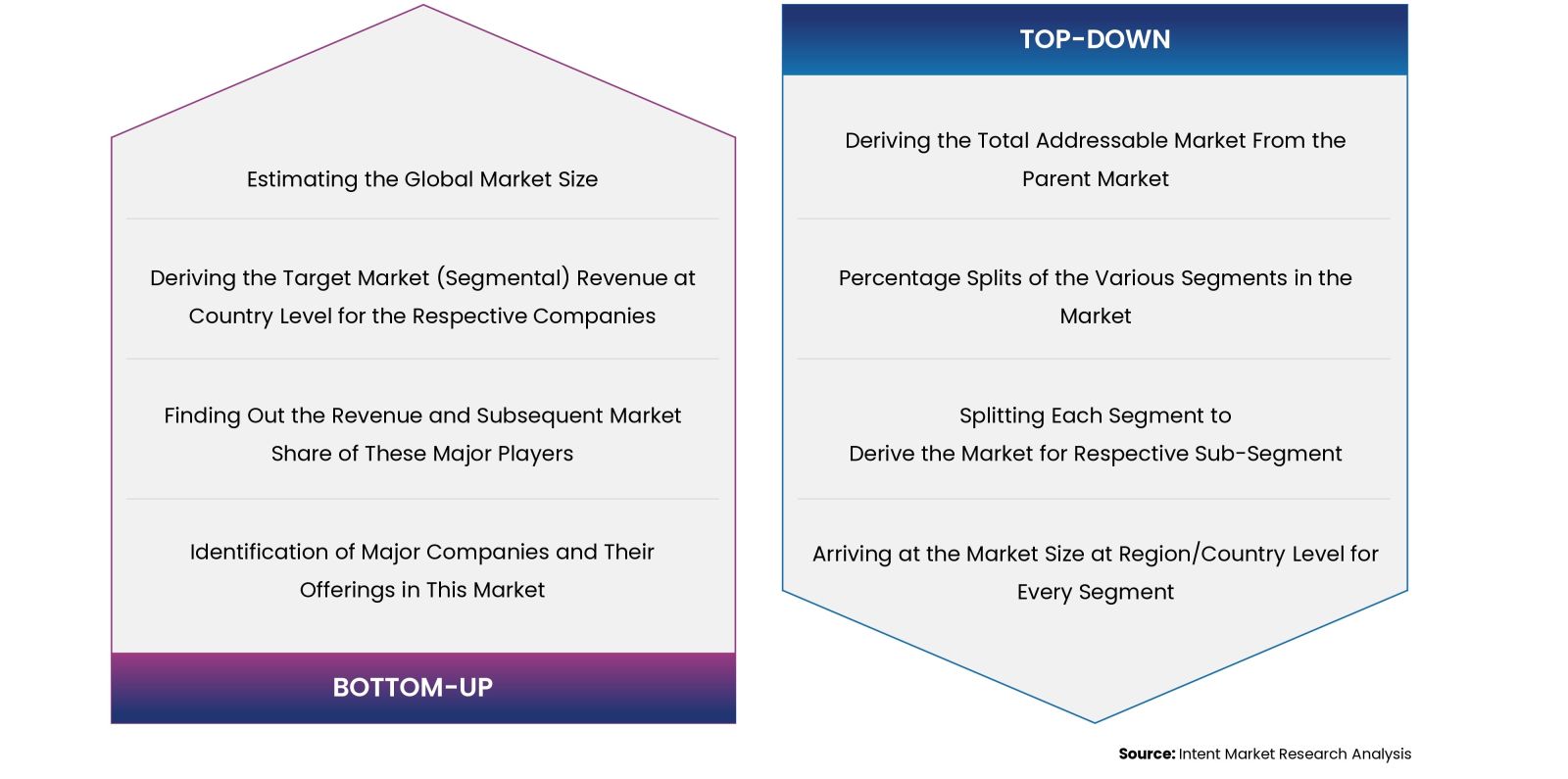

Available Formats


