As per Intent Market Research, the Wireless Infrastructure Market was valued at USD 175.9 billion in 2023 and will surpass USD 406.9 billion by 2030; growing at a CAGR of 12.7% during 2024 - 2030.
The wireless infrastructure market plays a crucial role in enabling seamless communication across the globe. With the rise of data-driven services and mobile connectivity, the demand for robust and scalable wireless infrastructure has surged. Key factors driving this growth include the ongoing 5G rollout, rising demand for high-speed internet, and the proliferation of smart devices. As telecom operators, governments, and enterprises invest in next-generation technologies, wireless infrastructure is becoming increasingly essential in supporting a wide range of applications, including 5G, smart cities, and industrial automation.
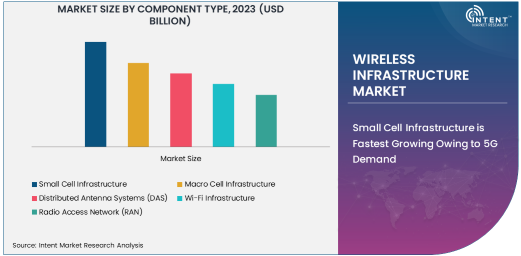
Small Cell Infrastructure is Fastest Growing Owing to 5G Demand
Small cell infrastructure is the fastest-growing subsegment within the wireless infrastructure market, primarily driven by the global rollout of 5G networks. Small cells are low-power, short-range wireless transmitters designed to augment cellular networks by boosting coverage and increasing capacity, particularly in dense urban environments. Unlike traditional macro cells, small cells are deployed in a decentralized manner, making them ideal for the heterogeneous network architecture needed for 5G. As 5G adoption accelerates, small cell infrastructure is seen as a vital component in ensuring seamless connectivity, improving data transfer speeds, and reducing network congestion in high-traffic areas.
With 5G networks requiring higher data throughput and lower latency, small cells are crucial in achieving the performance goals set by telecom providers. Their ability to integrate with existing networks, enhance user experience, and complement macro cell deployments makes them a preferred choice for the industry's future growth. This demand for small cell infrastructure is expected to continue rising, making it a key driver in the expansion of wireless infrastructure.
5G Technology is Largest Owing to Widespread Adoption
5G technology is the largest subsegment in the wireless infrastructure market, driven by the extensive global investments in 5G network buildouts. The transition from 4G to 5G is revolutionizing wireless connectivity, promising faster data speeds, ultra-low latency, and massive connectivity for devices. Telecommunication companies and service providers are heavily investing in 5G infrastructure, which requires advanced technologies like small cells, millimeter waves (MMWave), and massive MIMO antennas to meet the speed and capacity demands of next-generation networks.
The widespread deployment of 5G across various industries, including telecommunications, automotive, healthcare, and industrial sectors, has made it the dominant technology within the wireless infrastructure market. As the technology matures, it is expected that the demand for 5G-related infrastructure will continue to grow, further driving the development of new solutions and innovations in the market.
Residential Application is Largest Due to Rising Connectivity Needs
The residential application is the largest segment in the wireless infrastructure market, primarily driven by the increasing demand for high-speed internet and connected devices within homes. As smart home technologies, including IoT devices, smart speakers, and home automation systems, become more prevalent, the need for reliable and high-performance wireless connectivity is intensifying. Consumers are increasingly seeking faster internet speeds, seamless streaming capabilities, and better coverage within their homes, which drives the demand for advanced wireless infrastructure solutions such as Wi-Fi and 5G.
The growth of residential applications is also fueled by the rise of remote working and learning, which has further amplified the need for robust and reliable home networks. As more households adopt smart technologies and broadband services, wireless infrastructure becomes a critical enabler of modern living, thus continuing to lead the market in terms of demand.
Telecommunications Industry is Largest End-User Due to Network Expansion
The telecommunications industry is the largest end-user of wireless infrastructure, driven by the ongoing network expansion and the shift toward 5G. Telecom operators are investing heavily in upgrading and expanding their networks to meet the growing demand for high-speed internet and mobile data services. The deployment of new technologies, such as 5G, small cells, and fiber optic networks, is essential for supporting the vast amount of data generated by consumers, businesses, and connected devices.
Telecommunications companies are also focusing on improving network reliability and coverage, especially in underserved and rural areas. As competition increases among telecom providers and the demand for higher network performance intensifies, wireless infrastructure plays a critical role in supporting these initiatives, ensuring that operators can offer top-tier services to their customers.
Direct Sales is Dominant Distribution Channel Owing to High-Value Products
Direct sales is the dominant distribution channel in the wireless infrastructure market, largely because of the high-value and customized nature of the products involved. Components like small cells, distributed antenna systems (DAS), and radio access networks (RAN) require specialized sales channels that can offer tailored solutions for large-scale deployments. Telecom operators and large enterprises typically work directly with infrastructure vendors to ensure that the products meet their specific network requirements and integration needs.
The direct sales model also allows for long-term partnerships, as telecom companies often rely on network infrastructure providers for ongoing maintenance, upgrades, and technical support. This personalized approach ensures that buyers receive the most suitable products for their unique needs, making direct sales a key channel for wireless infrastructure market growth.
Asia-Pacific Region is Fastest Growing Due to 5G Rollout
The Asia-Pacific region is the fastest growing in the wireless infrastructure market, driven by the rapid expansion of 5G networks and the increasing demand for mobile data services. Countries like China, Japan, South Korea, and India are leading the charge in 5G deployment, and the region is home to some of the largest telecom operators, including China Mobile, SK Telecom, and NTT Docomo. These operators are investing heavily in advanced wireless technologies to support the growing digital economy and the rising number of connected devices in the region.
Additionally, the Asia-Pacific region is experiencing a surge in smart city initiatives, industrial IoT adoption, and the growth of consumer electronics, all of which contribute to the increasing demand for wireless infrastructure. As governments and private enterprises in the region continue to prioritize digital transformation and network modernization, Asia-Pacific is expected to maintain its position as the fastest-growing region in the wireless infrastructure market.

Competitive Landscape and Leading Companies
The wireless infrastructure market is highly competitive, with several leading companies driving innovation and growth. Key players in the market include Huawei Technologies, Ericsson, Nokia, Qualcomm, Cisco Systems, and Samsung Electronics. These companies are at the forefront of developing next-generation wireless technologies such as 5G, small cells, and millimeter wave technology, and they are making strategic investments to strengthen their market positions.
The competitive landscape is characterized by ongoing mergers and acquisitions, partnerships, and collaborations aimed at enhancing technological capabilities and expanding geographic reach. For instance, Ericsson and Nokia are working closely with telecom operators globally to deploy large-scale 5G networks, while Huawei continues to lead in 5G infrastructure in China and other key markets. The increasing demand for high-speed connectivity, driven by 5G and other advanced wireless applications, will continue to fuel competition in this space, with companies focusing on offering more efficient, scalable, and cost-effective solutions to meet the evolving needs of customers.
List of Leading Companies:
- Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
- Ericsson AB
- Nokia Corporation
- Qualcomm Technologies, Inc.
- ZTE Corporation
- Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- Intel Corporation
- CommScope Holding Company, Inc.
- Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson
- Alcatel-Lucent (Nokia)
- Adtran, Inc.
- Ciena Corporation
- Juniper Networks, Inc.
- Arista Networks, Inc.
Recent Developments:
- Ericsson has signed a multi-year deal with T-Mobile to expand their 5G radio network infrastructure, enhancing nationwide coverage and improving service delivery.
- Huawei has secured major contracts to provide 5G equipment and services for telecom operators across Europe, marking a significant step in the company’s global expansion.
- CommScope introduced its new distributed antenna system (DAS) designed to boost 5G network performance, offering advanced features tailored for high-density venues and smart city applications.
- Nokia has entered into a partnership with Telefonica to upgrade and expand the 5G network infrastructure across Spain, enhancing the network's reach and capacity.
- Qualcomm and Samsung are collaborating on next-generation 5G radio access network (RAN) technology, focusing on improved performance and cost-effective deployment for global 5G rollouts.
Report Scope:
|
Report Features |
Description |
|
Market Size (2023) |
USD 175.9 Billion |
|
Forecasted Value (2030) |
USD 406.9 Billion |
|
CAGR (2024 – 2030) |
12.7% |
|
Base Year for Estimation |
2023 |
|
Historic Year |
2022 |
|
Forecast Period |
2024 – 2030 |
|
Report Coverage |
Market Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments |
|
Segments Covered |
Wireless Infrastructure Market by Component Type (Small Cell Infrastructure, Macro Cell Infrastructure, Distributed Antenna Systems (DAS), Wi-Fi Infrastructure, Radio Access Network (RAN)), by Technology (4G LTE, 5G, Wi-Fi, Fixed Wireless Access (FWA), Millimeter Wave (MMWave) Technology), by Application (Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Public Sector, Entertainment and Media), by End-User Industry (Telecommunications, Consumer Electronics, Industrial Manufacturing, Automotive, Healthcare), by Distribution Channel (Direct Sales, Online Retail, Retailers, Distributors) |
|
Regional Analysis |
North America (US, Canada, Mexico), Europe (Germany, France, UK, Italy, Spain, and Rest of Europe), Asia-Pacific (China, Japan, South Korea, Australia, India, and Rest of Asia-Pacific), Latin America (Brazil, Argentina, and Rest of Latin America), Middle East & Africa (Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of Middle East & Africa) |
|
Major Companies |
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., Ericsson AB, Nokia Corporation, Qualcomm Technologies, Inc., ZTE Corporation, Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., Cisco Systems, Inc., Intel Corporation, CommScope Holding Company, Inc., Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson, Alcatel-Lucent (Nokia), Adtran, Inc., Ciena Corporation, Juniper Networks, Inc., Arista Networks, Inc. |
|
Customization Scope |
Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements |
|
1. Introduction |
|
1.1. Market Definition |
|
1.2. Scope of the Study |
|
1.3. Research Assumptions |
|
1.4. Study Limitations |
|
2. Research Methodology |
|
2.1. Research Approach |
|
2.1.1. Top-Down Method |
|
2.1.2. Bottom-Up Method |
|
2.1.3. Factor Impact Analysis |
|
2.2. Insights & Data Collection Process |
|
2.2.1. Secondary Research |
|
2.2.2. Primary Research |
|
2.3. Data Mining Process |
|
2.3.1. Data Analysis |
|
2.3.2. Data Validation and Revalidation |
|
2.3.3. Data Triangulation |
|
3. Executive Summary |
|
3.1. Major Markets & Segments |
|
3.2. Highest Growing Regions and Respective Countries |
|
3.3. Impact of Growth Drivers & Inhibitors |
|
3.4. Regulatory Overview by Country |
|
4. Wireless Infrastructure Market, by Component Type (Market Size & Forecast: USD Million, 2022 – 2030) |
|
4.1. Small Cell Infrastructure |
|
4.2. Macro Cell Infrastructure |
|
4.3. Distributed Antenna Systems (DAS) |
|
4.4. Wi-Fi Infrastructure |
|
4.5. Radio Access Network (RAN) |
|
5. Wireless Infrastructure Market, by Technology (Market Size & Forecast: USD Million, 2022 – 2030) |
|
5.1. 4G LTE |
|
5.2. 5G |
|
5.3. Wi-Fi |
|
5.4. Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) |
|
5.5. Millimeter Wave (MMWave) Technology |
|
6. Wireless Infrastructure Market, by Application (Market Size & Forecast: USD Million, 2022 – 2030) |
|
6.1. Residential |
|
6.2. Commercial |
|
6.3. Industrial |
|
6.4. Public Sector (Government, Defense) |
|
6.5. Entertainment and Media |
|
7. Wireless Infrastructure Market, by End-User Industry (Market Size & Forecast: USD Million, 2022 – 2030) |
|
7.1. Telecommunications |
|
7.2. Consumer Electronics |
|
7.3. Industrial Manufacturing |
|
7.4. Automotive |
|
7.5. Healthcare |
|
8. Wireless Infrastructure Market, by Distribution Channel (Market Size & Forecast: USD Million, 2022 – 2030) |
|
8.1. Direct Sales |
|
8.2. Online Retail |
|
8.3. Retailers |
|
8.4. Distributors |
|
9. Regional Analysis (Market Size & Forecast: USD Million, 2022 – 2030) |
|
9.1. Regional Overview |
|
9.2. North America |
|
9.2.1. Regional Trends & Growth Drivers |
|
9.2.2. Barriers & Challenges |
|
9.2.3. Opportunities |
|
9.2.4. Factor Impact Analysis |
|
9.2.5. Technology Trends |
|
9.2.6. North America Wireless Infrastructure Market, by Component Type |
|
9.2.7. North America Wireless Infrastructure Market, by Technology |
|
9.2.8. North America Wireless Infrastructure Market, by Application |
|
9.2.9. North America Wireless Infrastructure Market, by End-User Industry |
|
9.2.10. North America Wireless Infrastructure Market, by Distribution Channel |
|
9.2.11. By Country |
|
9.2.11.1. US |
|
9.2.11.1.1. US Wireless Infrastructure Market, by Component Type |
|
9.2.11.1.2. US Wireless Infrastructure Market, by Technology |
|
9.2.11.1.3. US Wireless Infrastructure Market, by Application |
|
9.2.11.1.4. US Wireless Infrastructure Market, by End-User Industry |
|
9.2.11.1.5. US Wireless Infrastructure Market, by Distribution Channel |
|
9.2.11.2. Canada |
|
9.2.11.3. Mexico |
|
*Similar segmentation will be provided for each region and country |
|
9.3. Europe |
|
9.4. Asia-Pacific |
|
9.5. Latin America |
|
9.6. Middle East & Africa |
|
10. Competitive Landscape |
|
10.1. Overview of the Key Players |
|
10.2. Competitive Ecosystem |
|
10.2.1. Level of Fragmentation |
|
10.2.2. Market Consolidation |
|
10.2.3. Product Innovation |
|
10.3. Company Share Analysis |
|
10.4. Company Benchmarking Matrix |
|
10.4.1. Strategic Overview |
|
10.4.2. Product Innovations |
|
10.5. Start-up Ecosystem |
|
10.6. Strategic Competitive Insights/ Customer Imperatives |
|
10.7. ESG Matrix/ Sustainability Matrix |
|
10.8. Manufacturing Network |
|
10.8.1. Locations |
|
10.8.2. Supply Chain and Logistics |
|
10.8.3. Product Flexibility/Customization |
|
10.8.4. Digital Transformation and Connectivity |
|
10.8.5. Environmental and Regulatory Compliance |
|
10.9. Technology Readiness Level Matrix |
|
10.10. Technology Maturity Curve |
|
10.11. Buying Criteria |
|
11. Company Profiles |
|
11.1. Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. |
|
11.1.1. Company Overview |
|
11.1.2. Company Financials |
|
11.1.3. Product/Service Portfolio |
|
11.1.4. Recent Developments |
|
11.1.5. IMR Analysis |
|
*Similar information will be provided for other companies |
|
11.2. Ericsson AB |
|
11.3. Nokia Corporation |
|
11.4. Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. |
|
11.5. ZTE Corporation |
|
11.6. Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. |
|
11.7. Cisco Systems, Inc. |
|
11.8. Intel Corporation |
|
11.9. CommScope Holding Company, Inc. |
|
11.10. Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson |
|
11.11. Alcatel-Lucent (Nokia) |
|
11.12. Adtran, Inc. |
|
11.13. Ciena Corporation |
|
11.14. Juniper Networks, Inc. |
|
11.15. Arista Networks, Inc. |
|
12. Appendix |
A comprehensive market research approach was employed to gather and analyze data on the Wireless Infrastructure Market. In the process, the analysis was also done to analyze the parent market and relevant adjacencies to measure the impact of them on the Wireless Infrastructure Market. The research methodology encompassed both secondary and primary research techniques, ensuring the accuracy and credibility of the findings.
.jpg)
Secondary Research
Secondary research involved a thorough review of pertinent industry reports, journals, articles, and publications. Additionally, annual reports, press releases, and investor presentations of industry players were scrutinized to gain insights into their market positioning and strategies.
Primary Research
Primary research involved conducting in-depth interviews with industry experts, stakeholders, and market participants across the E-Waste Management ecosystem. The primary research objectives included:
- Validating findings and assumptions derived from secondary research
- Gathering qualitative and quantitative data on market trends, drivers, and challenges
- Understanding the demand-side dynamics, encompassing end-users, component manufacturers, facility providers, and service providers
- Assessing the supply-side landscape, including technological advancements and recent developments
Market Size Assessment
A combination of top-down and bottom-up approaches was utilized to analyze the overall size of the Wireless Infrastructure Market. These methods were also employed to assess the size of various subsegments within the market. The market size assessment methodology encompassed the following steps:
- Identification of key industry players and relevant revenues through extensive secondary research
- Determination of the industry's supply chain and market size, in terms of value, through primary and secondary research processes
- Calculation of percentage shares, splits, and breakdowns using secondary sources and verification through primary sources
.jpg)
Data Triangulation
To ensure the accuracy and reliability of the market size, data triangulation was implemented. This involved cross-referencing data from various sources, including demand and supply side factors, market trends, and expert opinions. Additionally, top-down and bottom-up approaches were employed to validate the market size assessment.
NA
