As per Intent Market Research, the Voluntary Carbon Credit Market was valued at USD 3.2 Billion in 2024-e and will surpass USD 14.4 Billion by 2030; growing at a CAGR of 28.2% during 2025-2030.
The voluntary carbon credit market plays a pivotal role in global climate change mitigation efforts by enabling individuals, corporations, and government entities to offset their carbon emissions. Through the purchase of carbon credits, these entities invest in projects aimed at reducing or capturing greenhouse gases (GHGs). The market has seen significant growth due to the increasing urgency for climate action, evolving regulatory frameworks, and the growing awareness of the need for environmental sustainability. Organizations across various industries are now prioritizing carbon offsetting strategies to meet their environmental goals, making the voluntary carbon credit market an essential component of the global effort to combat climate change.
The voluntary carbon credit market encompasses a wide range of project types, including carbon offset projects, carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies, renewable energy initiatives, and forestry and land-use projects. With the rise of corporate sustainability efforts and regulatory pressures, demand for voluntary carbon credits continues to surge. Market participants are increasingly investing in carbon offset programs that provide measurable environmental impact while contributing to local and global sustainability goals. The market is also seeing growth in financial institutions and government agencies that aim to meet emission reduction targets through the purchase of carbon credits.
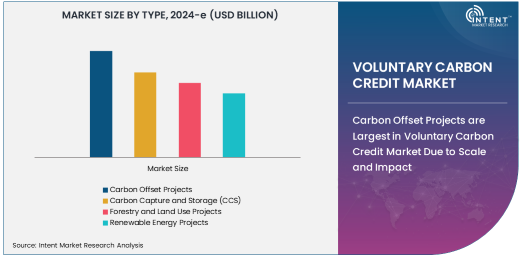
Carbon Offset Projects are Largest in Voluntary Carbon Credit Market Due to Scale and Impact
Carbon Offset Projects, particularly in the form of forestry and land-use initiatives, dominate the voluntary carbon credit market due to their large-scale impact on reducing carbon emissions. These projects, such as reforestation, afforestation, and sustainable land management, offer some of the most effective means of sequestering carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. The significant environmental benefits of these projects, coupled with their scalability, make them the most popular and impactful method for offsetting carbon emissions globally.
Forestry and land-use projects are often implemented in developing regions, such as Africa, Latin America, and Southeast Asia, where large tracts of land are available for reforestation and sustainable land management. These projects not only reduce carbon emissions but also provide socioeconomic benefits, such as job creation, improved livelihoods, and biodiversity conservation. As companies and governments commit to achieving net-zero emissions, forestry and land-use projects continue to form the backbone of the voluntary carbon credit market, especially in the context of corporate carbon offsetting strategies.
Corporations Drive Demand for Voluntary Carbon Credits to Meet Sustainability Goals
Corporations are the largest end-users of voluntary carbon credits as they increasingly adopt sustainability practices to meet their environmental commitments. Large organizations across industries such as manufacturing, transportation, and energy are purchasing carbon credits to offset their operational emissions. The growing regulatory pressures and rising public awareness regarding climate change have pushed corporations to take more proactive steps in their environmental responsibility.
These companies typically invest in carbon offset projects to reduce their carbon footprint while fulfilling the requirements of sustainability certifications, industry standards, and government regulations. Many corporations are also aligning their carbon offsetting efforts with their corporate social responsibility (CSR) goals, positioning themselves as leaders in the fight against climate change. With many multinational corporations committing to achieving net-zero emissions in the coming decades, demand for voluntary carbon credits will continue to rise.
Corporate Carbon Offsetting and Compliance with Environmental Standards Propel Market Growth
Corporate carbon offsetting and compliance with environmental standards are driving the market's growth. Companies in various sectors are using voluntary carbon credits to mitigate their carbon emissions and meet environmental regulations, standards, and sustainability certifications. Carbon credits allow organizations to balance their carbon footprint, especially in industries where emissions are hard to avoid or reduce directly, such as manufacturing and logistics.
As regulatory frameworks around carbon emissions tighten globally, the adoption of voluntary carbon credits by corporations for compliance with sustainability standards has surged. These credits not only help businesses meet local and international environmental laws but also provide them with the flexibility to offset emissions from various sources, contributing to their broader environmental risk management strategies.
Developing Regions See Significant Investment in Carbon Offset Projects
Developing regions such as Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America are at the forefront of carbon offset project development. These regions offer significant opportunities for large-scale carbon offset initiatives, including reforestation, renewable energy installations, and sustainable agriculture practices. The affordability of land, coupled with a favorable climate for carbon sequestration, makes developing regions ideal locations for carbon offset projects that can have a significant global impact.
In addition to their environmental benefits, these carbon offset projects provide substantial socio-economic advantages, including job creation, infrastructure development, and access to clean energy. As companies in developed regions look to offset their carbon emissions, developing regions are becoming key locations for investment, further driving the growth of the voluntary carbon credit market.
Verified Carbon Standard (VCS) Leads the Market for Credible Carbon Credit Certification
The Verified Carbon Standard (VCS) is the most widely used and trusted certification standard in the voluntary carbon credit market. VCS provides transparency and ensures that carbon offset projects produce real, measurable, and permanent emission reductions. Projects certified under VCS are independently verified to meet rigorous environmental standards, making them highly attractive to corporations and organizations seeking credible and effective carbon offset solutions.
VCS-certified projects are primarily in forestry, renewable energy, and land-use change, and the standard’s broad global acceptance further strengthens its position in the market. Although other certification standards, such as the Gold Standard and the American Carbon Registry (ACR), are also prevalent, VCS remains dominant due to its credibility, independence, and rigorous verification process.
North America Leads the Voluntary Carbon Credit Market Due to Strong Demand from Corporations and Financial Institutions
North America is the largest and most active region in the voluntary carbon credit market. The region’s leadership can be attributed to its robust regulatory frameworks, strong commitment to environmental sustainability, and the presence of major corporations across industries such as energy, manufacturing, and transportation. These corporations are significant consumers of voluntary carbon credits, using them to offset emissions and meet their sustainability goals.
In North America, both the United States and Canada are key players, with large-scale corporations leading the charge in carbon credit purchases. The region also hosts several prominent carbon credit certification bodies, including the Verified Carbon Standard (VCS), further solidifying its position as a hub for the voluntary carbon credit market. As regulatory frameworks in North America become more stringent, the demand for carbon credits is expected to continue rising, with both the private and public sectors increasingly turning to these credits to meet their climate goals.

Competitive Landscape of the Voluntary Carbon Credit Market
The voluntary carbon credit market is highly competitive, with a range of players involved in the development, certification, and trading of carbon credits. Leading organizations, such as South Pole Group, EcoAct, and Natural Capital Partners, specialize in carbon offset projects, carbon capture solutions, and sustainability consulting. These companies are at the forefront of the market, helping corporations and government entities achieve their carbon offsetting goals.
The market is also seeing increased participation from financial institutions and NGOs that invest in carbon credit projects to align with their environmental goals. Moreover, emerging technologies, such as blockchain for carbon credit verification and trading platforms, are changing the competitive landscape. Companies in the market are focusing on providing high-quality, verifiable carbon credits that meet the strict standards of international certification bodies like VCS, Gold Standard, and ACR. The growing interest in sustainability, coupled with advancements in technology and monitoring, will continue to shape the future of the voluntary carbon credit market.
Recent Developments:
- In December 2024, South Pole Group launched a new carbon credit verification system that enhances transparency in emission reductions.
- In November 2024, Microsoft committed to purchasing an additional 5 million voluntary carbon credits to support its carbon neutrality goals.
- In October 2024, Shell expanded its carbon offsetting initiatives by investing in reforestation and renewable energy projects worldwide.
- In September 2024, Verra introduced a new framework for certifying carbon credits from industrial decarbonization projects.
- In August 2024, Gold Standard Foundation rolled out new guidelines for integrating biodiversity benefits into carbon offset projects.
List of Leading Companies:
- South Pole Group,
- Natural Capital Partners,
- ClimatePartner,
- Verra,
- Gold Standard Foundation,
- The CarbonNeutral Company,
- EcoAct,
- Carbon Trust,
- First Climate,
- SCS Global Services,
- Deloitte,
- Walmart,
- Microsoft,
- BP,
- Shell
Report Scope:
|
Report Features |
Description |
|
Market Size (2024-e) |
USD 3.2 Billion |
|
Forecasted Value (2030) |
USD 14.4 Billion |
|
CAGR (2025 – 2030) |
28.2% |
|
Base Year for Estimation |
2024-e |
|
Historic Year |
2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 – 2030 |
|
Report Coverage |
Market Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments |
|
Segments Covered |
Voluntary Carbon Credit Market by Type (Carbon Offset Projects, Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS), Forestry and Land Use Projects, Renewable Energy Projects), End-User (Corporations, Government Agencies, NGOs and Nonprofits, Financial Institutions), Application (Corporate Carbon Offsetting, Compliance with Environmental Standards, Investment in Sustainable Projects, Environmental Risk Management), Project Location (Developing Regions, Developed Regions), Carbon Credit Type (Verified Carbon Standard (VCS), Gold Standard, American Carbon Registry (ACR)) |
|
Regional Analysis |
North America (US, Canada, Mexico), Europe (Germany, France, UK, Italy, Spain, and Rest of Europe), Asia-Pacific (China, Japan, South Korea, Australia, India, and Rest of Asia-Pacific), Latin America (Brazil, Argentina, and Rest of Latin America), Middle East & Africa (Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of Middle East & Africa) |
|
Major Companies |
South Pole Group, Natural Capital Partners, ClimatePartner, Verra, Gold Standard Foundation, The CarbonNeutral Company, EcoAct, Carbon Trust, First Climate, SCS Global Services, Deloitte, Walmart, Microsoft, BP, Shell |
|
Customization Scope |
Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements |
|
1. Introduction |
|
1.1. Market Definition |
|
1.2. Scope of the Study |
|
1.3. Research Assumptions |
|
1.4. Study Limitations |
|
2. Research Methodology |
|
2.1. Research Approach |
|
2.1.1. Top-Down Method |
|
2.1.2. Bottom-Up Method |
|
2.1.3. Factor Impact Analysis |
|
2.2. Insights & Data Collection Process |
|
2.2.1. Secondary Research |
|
2.2.2. Primary Research |
|
2.3. Data Mining Process |
|
2.3.1. Data Analysis |
|
2.3.2. Data Validation and Revalidation |
|
2.3.3. Data Triangulation |
|
3. Executive Summary |
|
3.1. Major Markets & Segments |
|
3.2. Highest Growing Regions and Respective Countries |
|
3.3. Impact of Growth Drivers & Inhibitors |
|
3.4. Regulatory Overview by Country |
|
4. Voluntary Carbon Credit Market, by Type (Market Size & Forecast: USD Million, 2023 – 2030) |
|
4.1. Carbon Offset Projects |
|
4.2. Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) |
|
4.3. Forestry and Land Use Projects |
|
4.4. Renewable Energy Projects |
|
5. Voluntary Carbon Credit Market, by End-User (Market Size & Forecast: USD Million, 2023 – 2030) |
|
5.1. Corporations |
|
5.2. Government Agencies |
|
5.3. NGOs and Nonprofits |
|
5.4. Financial Institutions |
|
6. Voluntary Carbon Credit Market, by Application (Market Size & Forecast: USD Million, 2023 – 2030) |
|
6.1. Corporate Carbon Offsetting |
|
6.2. Compliance with Environmental Standards |
|
6.3. Investment in Sustainable Projects |
|
6.4. Environmental Risk Management |
|
7. Voluntary Carbon Credit Market, by Project Location (Market Size & Forecast: USD Million, 2023 – 2030) |
|
7.1. Developing Regions |
|
7.2. Developed Regions |
|
8. Voluntary Carbon Credit Market, by Carbon Credit Type (Market Size & Forecast: USD Million, 2023 – 2030) |
|
8.1. Verified Carbon Standard (VCS) |
|
8.2. Gold Standard |
|
8.3. American Carbon Registry (ACR) |
|
9. Regional Analysis (Market Size & Forecast: USD Million, 2023 – 2030) |
|
9.1. Regional Overview |
|
9.2. North America |
|
9.2.1. Regional Trends & Growth Drivers |
|
9.2.2. Barriers & Challenges |
|
9.2.3. Opportunities |
|
9.2.4. Factor Impact Analysis |
|
9.2.5. Technology Trends |
|
9.2.6. North America Voluntary Carbon Credit Market, by Type |
|
9.2.7. North America Voluntary Carbon Credit Market, by End-User |
|
9.2.8. North America Voluntary Carbon Credit Market, by Application |
|
9.2.9. North America Voluntary Carbon Credit Market, by Project Location |
|
9.2.10. By Country |
|
9.2.10.1. US |
|
9.2.10.1.1. US Voluntary Carbon Credit Market, by Type |
|
9.2.10.1.2. US Voluntary Carbon Credit Market, by End-User |
|
9.2.10.1.3. US Voluntary Carbon Credit Market, by Application |
|
9.2.10.1.4. US Voluntary Carbon Credit Market, by Project Location |
|
9.2.10.2. Canada |
|
9.2.10.3. Mexico |
|
*Similar segmentation will be provided for each region and country |
|
9.3. Europe |
|
9.4. Asia-Pacific |
|
9.5. Latin America |
|
9.6. Middle East & Africa |
|
10. Competitive Landscape |
|
10.1. Overview of the Key Players |
|
10.2. Competitive Ecosystem |
|
10.2.1. Level of Fragmentation |
|
10.2.2. Market Consolidation |
|
10.2.3. Product Innovation |
|
10.3. Company Share Analysis |
|
10.4. Company Benchmarking Matrix |
|
10.4.1. Strategic Overview |
|
10.4.2. Product Innovations |
|
10.5. Start-up Ecosystem |
|
10.6. Strategic Competitive Insights/ Customer Imperatives |
|
10.7. ESG Matrix/ Sustainability Matrix |
|
10.8. Manufacturing Network |
|
10.8.1. Locations |
|
10.8.2. Supply Chain and Logistics |
|
10.8.3. Product Flexibility/Customization |
|
10.8.4. Digital Transformation and Connectivity |
|
10.8.5. Environmental and Regulatory Compliance |
|
10.9. Technology Readiness Level Matrix |
|
10.10. Technology Maturity Curve |
|
10.11. Buying Criteria |
|
11. Company Profiles |
|
11.1. South Pole Group |
|
11.1.1. Company Overview |
|
11.1.2. Company Financials |
|
11.1.3. Product/Service Portfolio |
|
11.1.4. Recent Developments |
|
11.1.5. IMR Analysis |
|
*Similar information will be provided for other companies |
|
11.2. Natural Capital Partners |
|
11.3. ClimatePartner |
|
11.4. Verra |
|
11.5. Gold Standard Foundation |
|
11.6. The CarbonNeutral Company |
|
11.7. EcoAct |
|
11.8. Carbon Trust |
|
11.9. First Climate |
|
11.10. SCS Global Services |
|
11.11. Deloitte |
|
11.12. Walmart |
|
11.13. Microsoft |
|
11.14. BP |
|
11.15. Shell |
|
12. Appendix |
A comprehensive market research approach was employed to gather and analyze data on the Voluntary Carbon Credit Market. In the process, the analysis was also done to analyze the parent market and relevant adjacencies to measure the impact of them on the Voluntary Carbon Credit Market. The research methodology encompassed both secondary and primary research techniques, ensuring the accuracy and credibility of the findings.
.jpg)
Secondary Research
Secondary research involved a thorough review of pertinent industry reports, journals, articles, and publications. Additionally, annual reports, press releases, and investor presentations of industry players were scrutinized to gain insights into their market positioning and strategies.
Primary Research
Primary research involved conducting in-depth interviews with industry experts, stakeholders, and market participants across the E-Waste Management ecosystem. The primary research objectives included:
- Validating findings and assumptions derived from secondary research
- Gathering qualitative and quantitative data on market trends, drivers, and challenges
- Understanding the demand-side dynamics, encompassing end-users, component manufacturers, facility providers, and service providers
- Assessing the supply-side landscape, including technological advancements and recent developments
Market Size Assessment
A combination of top-down and bottom-up approaches was utilized to analyze the overall size of the Voluntary Carbon Credit Market. These methods were also employed to assess the size of various subsegments within the market. The market size assessment methodology encompassed the following steps:
- Identification of key industry players and relevant revenues through extensive secondary research
- Determination of the industry's supply chain and market size, in terms of value, through primary and secondary research processes
- Calculation of percentage shares, splits, and breakdowns using secondary sources and verification through primary sources
.jpg)
Data Triangulation
To ensure the accuracy and reliability of the market size, data triangulation was implemented. This involved cross-referencing data from various sources, including demand and supply side factors, market trends, and expert opinions. Additionally, top-down and bottom-up approaches were employed to validate the market size assessment.
NA
