As per Intent Market Research, the Smart Cities Market was valued at USD 572.6 billion in 2023 and will surpass USD 931.4 billion by 2030; growing at a CAGR of 7.2% during 2024 - 2030.

The smart cities market is a rapidly evolving sector that integrates advanced technologies and data-driven solutions to enhance urban living, sustainability, and governance. As urbanization continues to rise globally, cities are facing significant challenges, including traffic congestion, pollution, and resource management. Smart cities aim to address these challenges through the implementation of smart technologies such as Internet of Things (IoT) devices, big data analytics, and artificial intelligence (AI). These technologies empower city planners and administrators to create more efficient infrastructures, improve public services, and enhance the quality of life for residents.
This growth is driven by increasing investments in smart infrastructure, government initiatives for urban development, and the rising demand for sustainable living solutions. The base year for this analysis is 2024, with the market expected to gain momentum as cities increasingly adopt smart technologies.
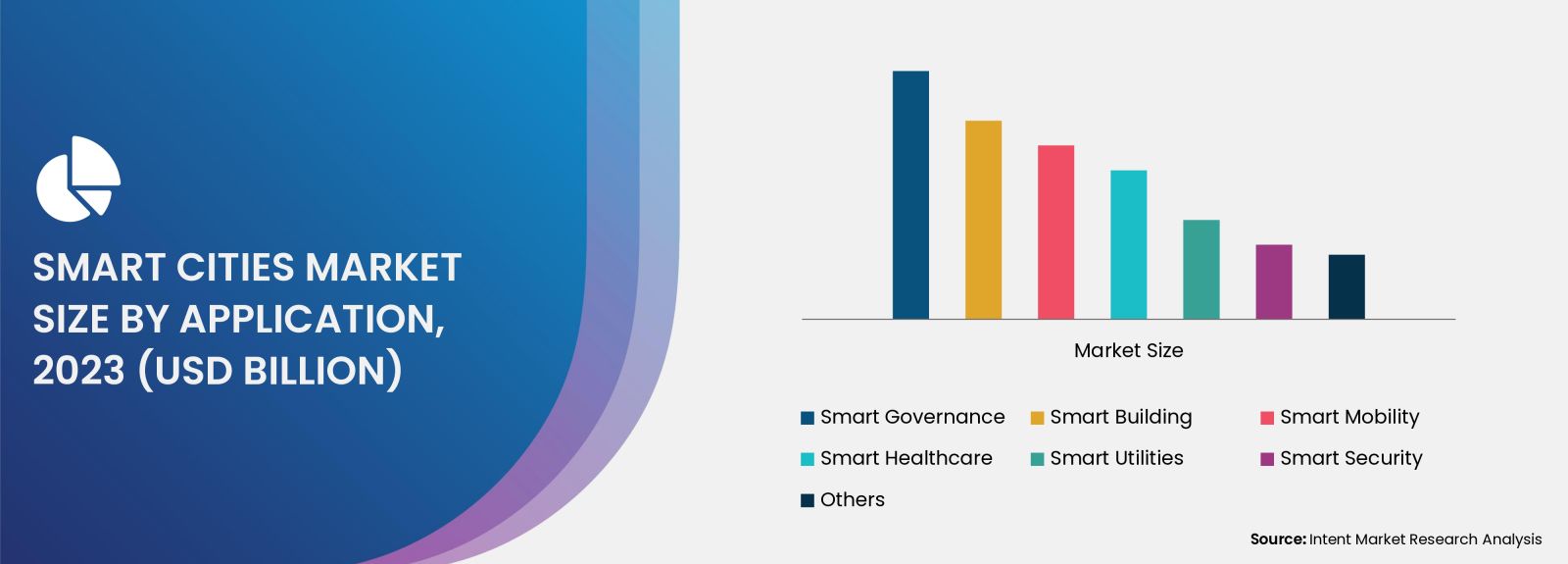
Smart Infrastructure Segment is Largest Owing to Increased Urbanization
The smart infrastructure segment stands as the largest in the smart cities market, primarily driven by the accelerating pace of urbanization. As more people migrate to urban areas, the demand for efficient infrastructure solutions becomes paramount. Smart infrastructure encompasses a range of technologies, including smart grid systems, intelligent transportation networks, and advanced waste management solutions. These technologies not only improve operational efficiencies but also contribute to significant cost savings and enhanced service delivery.
Furthermore, governments worldwide are increasingly investing in upgrading existing infrastructure to incorporate smart technologies. Initiatives such as the development of smart roads, bridges equipped with sensors, and automated traffic management systems are being prioritized. For instance, cities like Singapore and Barcelona have already implemented smart infrastructure projects that facilitate real-time monitoring and management of urban systems. This trend is expected to continue, with smart infrastructure remaining at the forefront of the smart cities market.
Smart Transportation Segment is Fastest Growing Owing to Demand for Mobility Solutions
The smart transportation segment is the fastest-growing sector within the smart cities market, driven by the urgent need for efficient mobility solutions. With urban populations expanding, cities are grappling with severe traffic congestion and pollution issues. Smart transportation incorporates technologies such as connected vehicles, intelligent traffic management systems, and public transit optimization solutions. These innovations aim to enhance mobility, reduce travel times, and minimize environmental impacts.
The rise of electric and autonomous vehicles is also significantly contributing to the growth of this segment. With increasing concerns over carbon emissions and the need for sustainable transport options, cities are investing in infrastructure that supports electric vehicle charging and promotes shared mobility solutions. The integration of data analytics and IoT in transportation systems allows for real-time monitoring and adaptive traffic management, making this segment crucial for future urban mobility strategies. As a result, the smart transportation segment is expected to witness remarkable growth, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Smart Energy Segment is Largest Owing to Sustainability Initiatives
The smart energy segment emerges as the largest contributor to the overall smart cities market, driven by increasing sustainability initiatives and the need for efficient energy management. Smart energy solutions, including smart grids, renewable energy integration, and energy storage systems, enable cities to optimize energy consumption and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. The transition to renewable energy sources is a focal point for many urban areas striving to become more sustainable.
Moreover, government policies and incentives aimed at promoting clean energy adoption further bolster the smart energy segment. For example, cities are implementing smart meters and energy management systems that provide consumers with real-time data on energy usage, encouraging energy conservation. The collaboration between municipal governments and energy companies is fostering innovative solutions that enhance energy efficiency and reliability, solidifying smart energy's position as a pivotal element in the smart cities market.
Smart Buildings Segment is Fastest Growing Owing to Technological Advancements
The smart buildings segment is the fastest-growing area in the smart cities market, propelled by technological advancements and a growing emphasis on sustainability. Smart buildings leverage IoT devices, automation systems, and energy-efficient technologies to create environments that enhance occupant comfort, optimize energy use, and reduce operational costs. Features such as smart lighting, HVAC control, and occupancy sensors are increasingly being integrated into new and existing buildings.
The rising demand for green building certifications and sustainable construction practices is further accelerating the growth of this segment. Building owners and developers are recognizing the benefits of smart technologies in achieving energy efficiency and reducing operational expenses. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic has heightened awareness regarding indoor air quality and health, prompting investments in smart building solutions that prioritize occupant well-being. As a result, the smart buildings segment is poised for rapid growth as urban areas adapt to evolving demands and technologies.
Smart Water Management Segment is Largest Owing to Water Scarcity Concerns
The smart water management segment is the largest within the smart cities market, primarily driven by growing concerns over water scarcity and the need for efficient water resource management. Smart water management solutions utilize IoT sensors, data analytics, and real-time monitoring systems to optimize water distribution, reduce waste, and enhance the overall efficiency of water services. These solutions are crucial for cities grappling with aging infrastructure and increasing water demand.
Furthermore, the implementation of smart water meters allows consumers to monitor their water usage, encouraging conservation efforts. Governments are also investing in smart irrigation systems to enhance agricultural water efficiency, addressing the challenges posed by climate change and population growth. As cities prioritize sustainable water management practices, the smart water management segment is expected to witness continued growth and innovation.
Smart Public Safety Segment is Fastest Growing Owing to Security Needs
The smart public safety segment is the fastest-growing area within the smart cities market, driven by increasing security needs and advancements in technology. Cities are increasingly adopting smart public safety solutions that utilize AI, video surveillance, and real-time data analytics to enhance security and emergency response capabilities. These technologies facilitate more effective crime prevention and management, providing law enforcement with valuable insights.
Moreover, the COVID-19 pandemic has heightened awareness of public safety, leading to increased investments in smart safety solutions. For instance, cities are implementing smart streetlights equipped with cameras and sensors to monitor public spaces and respond to emergencies promptly. The growing emphasis on citizen safety and the need for data-driven decision-making will propel the smart public safety segment's growth in the coming years, creating safer urban environments.
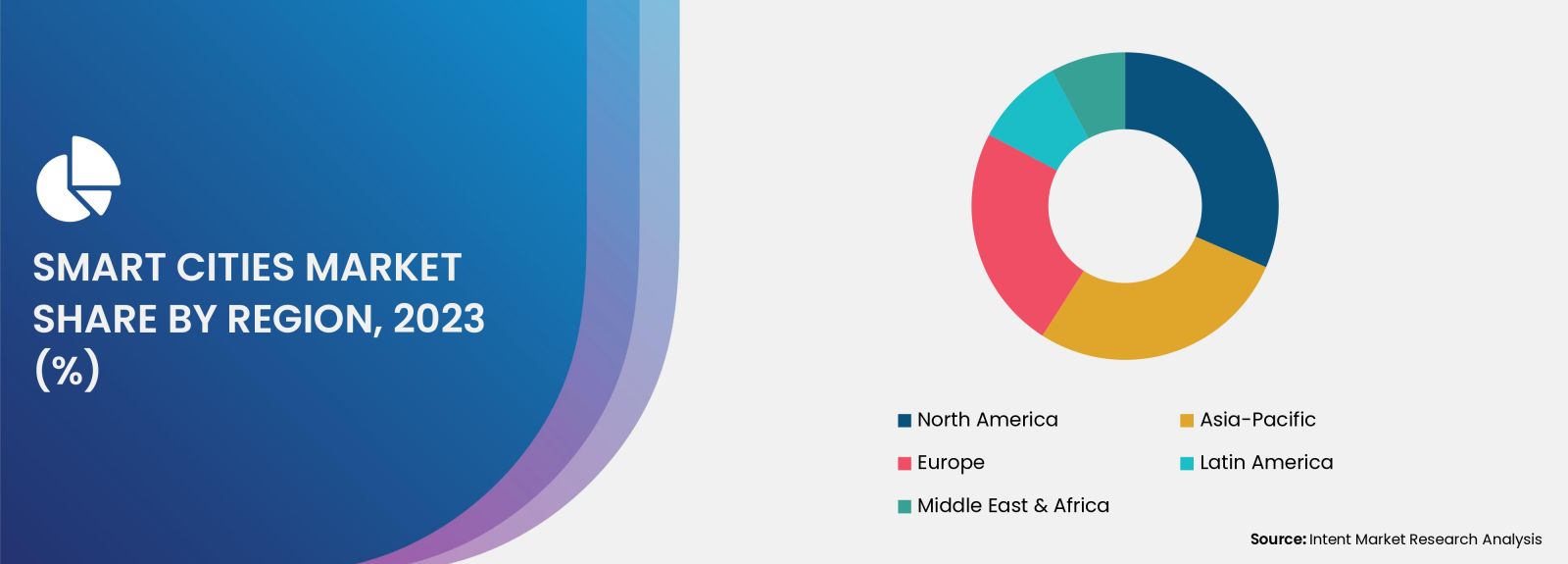
Asia-Pacific Region is Fastest Growing Owing to Rapid Urbanization
The Asia-Pacific region stands out as the fastest-growing market for smart cities, driven by rapid urbanization and increasing government initiatives to develop sustainable urban environments. Countries such as China, India, and Japan are leading the way in adopting smart city technologies, investing heavily in infrastructure development and digital solutions. The region's urban population is projected to reach 1.5 billion by 2030, intensifying the need for smart solutions to manage urban challenges effectively.
Governments in the Asia-Pacific region are launching smart city projects that prioritize sustainable development, improving transportation systems, energy management, and public safety. Initiatives like China's "Smart City Pilot Program" and India's "Smart Cities Mission" are examples of governmental efforts aimed at transforming urban areas into smart, connected cities. As cities in the Asia-Pacific region continue to embrace technology-driven solutions, the market for smart cities is expected to expand significantly.
Competitive Landscape and Leading Companies
The smart cities market is characterized by a highly competitive landscape, with several key players leading the charge in developing innovative technologies and solutions. Prominent companies in this sector include IBM, Cisco Systems, Siemens, Schneider Electric, and Microsoft. These companies are at the forefront of providing smart city solutions, encompassing smart infrastructure, energy management, transportation, and public safety.
The competitive dynamics in the smart cities market are shaped by strategic partnerships, collaborations, and acquisitions. Many companies are forging alliances with local governments, technology providers, and research institutions to enhance their offerings and expand their market reach. Additionally, the focus on sustainability and environmental responsibility is driving companies to innovate and develop solutions that align with global sustainability goals. As the market continues to evolve, collaboration and innovation will play pivotal roles in shaping the future of smart cities.
Report Objectives:
The report will help you answer some of the most critical questions in the Smart Cities Market. A few of them are as follows:
- What are the key drivers, restraints, opportunities, and challenges influencing the market growth?
- What are the prevailing technology trends in the Smart Cities Market?
- What is the size of the Smart Cities Market based on segments, sub-segments, and regions?
- What is the size of different market segments across key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa?
- What are the market opportunities for stakeholders after analyzing key market trends?
- Who are the leading market players and what are their market share and core competencies?
- What is the degree of competition in the market and what are the key growth strategies adopted by leading players?
- What is the competitive landscape of the market, including market share analysis, revenue analysis, and a ranking of key players?
Report Scope:
|
Report Features |
Description |
|
Market Size (2023) |
USD 572.6 billion |
|
Forecasted Value (2030) |
USD 931.4 billion |
|
CAGR (2024 – 2030) |
7.2% |
|
Base Year for Estimation |
2023 |
|
Historic Year |
2022 |
|
Forecast Period |
2024 – 2030 |
|
Report Coverage |
Market Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments |
|
Segments Covered |
Smart Cities Market By Component (Hardware, Software & Services), By Application (Smart Governance, Smart Building, Smart Mobility, Smart Healthcare, Smart Utilities, Smart Security), and By End User (Government and Public Services, Transportation, Utilities, Healthcare, Education, Residential, Commercial and Industrial) |
|
Regional Analysis |
North America (US, Canada, Mexico), Europe (Germany, France, UK, Italy, Spain, and Rest of Europe), Asia-Pacific (China, Japan, South Korea, Australia, India, and Rest of Asia-Pacific), Latin America (Brazil, Argentina, and Rest of Latin America), Middle East & Africa (Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of Middle East & Africa) |
|
Customization Scope |
Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements |
|
1. Introduction |
|
1.1. Market Definition |
|
1.2. Scope of the Study |
|
1.3. Research Assumptions |
|
1.4. Study Limitations |
|
2. Research Methodology |
|
2.1. Research Approach |
|
2.1.1. Top-Down Method |
|
2.1.2. Bottom-Up Method |
|
2.1.3. Factor Impact Analysis |
|
2.2. Insights & Data Collection Process |
|
2.2.1. Secondary Research |
|
2.2.2. Primary Research |
|
2.3. Data Mining Process |
|
2.3.1. Data Analysis |
|
2.3.2. Data Validation and Revalidation |
|
2.3.3. Data Triangulation |
|
3. Executive Summary |
|
3.1. Major Markets & Segments |
|
3.2. Highest Growing Regions and Respective Countries |
|
3.3. Impact of Growth Drivers & Inhibitors |
|
3.4. Regulatory Overview by Country |
|
4. Smart Cities Market, by Component (Market Size & Forecast: USD Million, 2022 – 2030) |
|
4.1. Hardware |
|
4.2. Software & Services |
|
5. Smart Cities Market, by Application (Market Size & Forecast: USD Million, 2022 – 2030) |
|
5.1. Smart Governance |
|
5.1.1. E-Government Services |
|
5.1.2. Online Education Platforms |
|
5.1.3. Others |
|
5.2. Smart Building |
|
5.2.1. Smart Homes |
|
5.2.2. Smart Offices |
|
5.2.3. Others |
|
5.3. Smart Mobility |
|
5.3.1. Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) |
|
5.3.2. Traffic Management Systems |
|
5.3.3. Shared Mobility Solutions |
|
5.3.4. Others |
|
5.4. Smart Healthcare |
|
5.4.1. Telemedicine |
|
5.4.2. Remote Patient Monitoring |
|
5.4.3. Healthcare Information Systems |
|
5.4.4. Others |
|
5.5. Smart Utilities |
|
5.5.1. Smart Grids |
|
5.5.2. Smart Water Management |
|
5.5.3. Smart Waste Management |
|
5.5.4. Others |
|
5.6. Smart Security |
|
5.6.1. Surveillance Systems |
|
5.6.2. Cybersecurity Solutions |
|
5.6.3. Emergency Response Systems |
|
5.6.4. Others |
|
5.7. Others |
|
6. Smart Cities Market, by End User (Market Size & Forecast: USD Million, 2022 – 2030) |
|
6.1. Government and Public Services |
|
6.2. Transportation |
|
6.3. Utilities |
|
6.4. Healthcare |
|
6.5. Education |
|
6.6. Residential |
|
6.7. Commercial and Industrial |
|
6.8. Others |
|
7. Regional Analysis (Market Size & Forecast: USD Million, 2022 – 2030) |
|
7.1. Regional Overview |
|
7.2. North America |
|
7.2.1. Regional Trends & Growth Drivers |
|
7.2.2. Barriers & Challenges |
|
7.2.3. Opportunities |
|
7.2.4. Factor Impact Analysis |
|
7.2.5. Technology Trends |
|
7.2.6. North America Smart Cities Market, by Component |
|
7.2.7. North America Smart Cities Market, by Application |
|
7.2.8. North America Smart Cities Market, by End User |
|
7.2.9. By Country |
|
7.2.9.1. US |
|
7.2.9.1.1. US Smart Cities Market, by Component |
|
7.2.9.1.2. US Smart Cities Market, by Application |
|
7.2.9.1.3. US Smart Cities Market, by End User |
|
7.2.9.2. Canada |
|
7.2.9.3. Mexico |
|
*Similar segmentation will be provided for each region and country |
|
7.3. Europe |
|
7.4. Asia-Pacific |
|
7.5. Latin America |
|
7.6. Middle East & Africa |
|
8. Competitive Landscape |
|
8.1. Overview of the Key Players |
|
8.2. Competitive Ecosystem |
|
8.2.1. Level of Fragmentation |
|
8.2.2. Market Consolidation |
|
8.2.3. Product Innovation |
|
8.3. Company Share Analysis |
|
8.4. Company Benchmarking Matrix |
|
8.4.1. Strategic Overview |
|
8.4.2. Product Innovations |
|
8.5. Start-up Ecosystem |
|
8.6. Strategic Competitive Insights/ Customer Imperatives |
|
8.7. ESG Matrix/ Sustainability Matrix |
|
8.8. Manufacturing Network |
|
8.8.1. Locations |
|
8.8.2. Supply Chain and Logistics |
|
8.8.3. Product Flexibility/Customization |
|
8.8.4. Digital Transformation and Connectivity |
|
8.8.5. Environmental and Regulatory Compliance |
|
8.9. Technology Readiness Level Matrix |
|
8.10. Technology Maturity Curve |
|
8.11. Buying Criteria |
|
9. Company Profiles |
|
9.1. ABB |
|
9.1.1. Company Overview |
|
9.1.2. Company Financials |
|
9.1.3. Product/Service Portfolio |
|
9.1.4. Recent Developments |
|
9.1.5. IMR Analysis |
|
*Similar information will be provided for other companies |
|
9.2. Cisco |
|
9.3. Ericsson |
|
9.4. General Electric |
|
9.5. Hitachi |
|
9.6. Honeywell |
|
9.7. Huawei |
|
9.8. IBM |
|
9.9. Intel |
|
9.10. Johnson Controls |
|
9.11. Microsoft |
|
9.12. Oracle |
|
9.13. SAP SE |
|
9.14. Schneider Electric |
|
9.15. Siemens |
|
10. Appendix |
A comprehensive market research approach was employed to gather and analyze data on the Smart Cities Market. In the process, the analysis was also done to analyze the parent market and relevant adjacencies to measure the impact of them on the Smart Cities Market. The research methodology encompassed both secondary and primary research techniques, ensuring the accuracy and credibility of the findings.
.jpg)
Secondary Research
Secondary research involved a thorough review of pertinent industry reports, journals, articles, and publications. Additionally, annual reports, press releases, and investor presentations of industry players were scrutinized to gain insights into their market positioning and strategies.
Primary Research
Primary research involved conducting in-depth interviews with industry experts, stakeholders, and market participants across the Smart Cities ecosystem. The primary research objectives included:
- Validating findings and assumptions derived from secondary research
- Gathering qualitative and quantitative data on market trends, drivers, and challenges
- Understanding the demand-side dynamics, encompassing end-users, component manufacturers, facility providers, and service providers
- Assessing the supply-side landscape, including technological advancements and recent developments
Market Size Assessment
A combination of top-down and bottom-up approaches was utilized to analyze the overall size of the Smart Cities Market. These methods were also employed to assess the size of various subsegments within the market. The market size assessment methodology encompassed the following steps:
- Identification of key industry players and relevant revenues through extensive secondary research
- Determination of the industry's supply chain and market size, in terms of value, through primary and secondary research processes
- Calculation of percentage shares, splits, and breakdowns using secondary sources and verification through primary sources
.jpg)
Data Triangulation
To ensure the accuracy and reliability of the market size, data triangulation was implemented. This involved cross-referencing data from various sources, including demand and supply side factors, market trends, and expert opinions. Additionally, top-down and bottom-up approaches were employed to validate the market size assessment.
NA
